Prof.T.Shivaji Rao,
Director,
Environmental studies,
GITAM University,Visakhapatnam,India
http://www.thehindu.com/multimedia/archive/00948/Concept_of_Defense-_948126a.pdf [dafety levels]
http://vorort.bund.net/suedlicher-oberrhein/pressurized-water-reactor-nuclear.html
(French view that a major accident is inevitable in any reactor)
http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/7180539.stm (New costs of nuclear power, BBC)
The guidelines, however, do not cover disasters resulting from a nuclear attack. An official said:
"The standard operating procedures to handle the aftermath of a nuclear attack have already been put in place by the defence ministry in consultation with other concerned departments and agencies."
http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2009-02-25/india/28036847_1_nuclear-reactors-ndma-civil-defence [Nuclear Bombing is handled by Defence ministry]
http://www.greenpeace.org/usa/en/news-and-blogs/campaign-blog/natural-disasters-the-silent-nuclear-threat/blog/37594/ [Nuclear plants are inherently hazardous,how?\]
http://factsanddetails.com/japan.php?itemid=2301&catid=23&subcatid=152#520
[Accident raised Nuclear costs by 20 percent]
Environmental studies,
GITAM University,Visakhapatnam,India
http://www.thehindu.com/multimedia/archive/00948/Concept_of_Defense-_948126a.pdf [dafety levels]
http://vorort.bund.net/suedlicher-oberrhein/pressurized-water-reactor-nuclear.html
(French view that a major accident is inevitable in any reactor)
http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/7180539.stm (New costs of nuclear power, BBC)
The guidelines, however, do not cover disasters resulting from a nuclear attack. An official said:
"The standard operating procedures to handle the aftermath of a nuclear attack have already been put in place by the defence ministry in consultation with other concerned departments and agencies."
http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2009-02-25/india/28036847_1_nuclear-reactors-ndma-civil-defence [Nuclear Bombing is handled by Defence ministry]
http://www.greenpeace.org/usa/en/news-and-blogs/campaign-blog/natural-disasters-the-silent-nuclear-threat/blog/37594/ [Nuclear plants are inherently hazardous,how?\]
http://factsanddetails.com/japan.php?itemid=2301&catid=23&subcatid=152#520
[Accident raised Nuclear costs by 20 percent]
http://nuclearfissionary.com/2010/04/02/comparing-energy-costs-of-nuclear-coal-gas-wind-and-solar/
[ comparitive costs of Nuclear,coal,Gas,wind Energies]
[ kudankulam fails as it withstands only Cessna & Learjets and not Boeings& Air Buses]
http://tribune.com.pk/story/478296/why-i-said-90-per-cent-of-indians-are-fools/ {Idiots-Indians?]}
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/05/120522134942.htm (Max Planck)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/nuregs/staff/sr1150/v1/sr1150v1-intro-and-part-1.pdf
[Explosion caases ocf FI VE rea ctors i n USA for disaster managemwent examples]
http://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyNET.exe/9100AE95.txt?ZyActionD=ZyDocument&Client=EPA&Index=1981%20Thru%201985&Docs=&Query=&Time=&EndTime=&SearchMethod=1&TocRestrict=n&Toc=&TocEntry=&QField=&QFieldYear=&QFieldMonth=&QFieldDay=&UseQField=&IntQFieldOp=0&ExtQFieldOp=0&XmlQuery=&File=D%3A\ZYFILES\INDEX%20DATA\81THRU85\TXT\00000016\9100AE95.txt&User=ANONYMOUS&Password=anonymous&SortMethod=h|-&MaximumDocuments=1&FuzzyDegree=0&ImageQuality=r75g8/r75g8/x150y150g16/i425&Display=p|f&DefSeekPage=x&SearchBack=ZyActionL&Back=ZyActionS&BackDesc=Results%20page&MaximumPages=1&ZyEntry=1
[AIR pollutioin Modelling Text Book ,lume Rise]
http://www.thehindu.com/multimedia/archive/00948/Concept_of_Defense-_948126a.pdf [Figure]
www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/.../Judgement-Kudankulam%20..
[Madras High Court Orders on Kudankulam Reactors,suggestin 30km.evacuation]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Japanese_reaction_to_Fukushima_Daiichi_nuclear_disaster
(Compensation to Victims by Japan is Rs.3 lakh crores + Evacuation events)
http://www.aerb.gov.in/T/PUBLICATIONS/CODESGUIDES/sg-s-1.pdf
(AERB on Radiation fall-out Modelling)
http://www.fema.gov/sites/default/files/orig/fema_pdfs/pdf/about/divisions/thd/rep_pg_manual_interim [ FEMA DISASTER panning ,EXCELLENT]
http://www.utsandiego.com/news/2011/apr/12/mock-nuclear-accident-drill-held-in-california/
[ MOCK DRILL FOR NUCLEAR DISASTER IN CALIFORNIA]
http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2149154/Catastrophic-nuclear-reactor-meltdowns-like-Chernobyl-Fukushima-happen-20-years-scientists-warn.html [probability of accidents]
http://news.blogs.cnn.com/2012/08/21/record-radiation-found-in-fish-near-fukushima-plant/
http://www.jfa.maff.go.jp/e/inspection/index.html (Fisheries pollution, Fukushima)
http://www.thehindu.com/news/states/tamil-nadu/sc-asks-tn-govt-to-submit-safety-plan-for-kknp/article4115720.ece [ SC asks Tamilnadu for Disaster plan Details of Mock-Drill]
http://www.shodor.org/cgi-bin/cascgi/plume.pl ]Gaussian model soft=ware for work]
http://ec.europa.eu/energy/nuclear/radioprotection/doc/studies/emergency_planning_en.pdf
(Source terms, DNA break, health impacts + EXCELLENT ARTICLE)
http://www.aerb.gov.in/T/PUBLICATIONS/CODESGUIDES/sg-s-1.pdf
(AERB guidelines for air pollution levels upto 30km, see item-1.3 under Introduction)
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/INES-2009_web.pdf- (Working Model for Event category)
http://www.thehindu.com/forum/comment.do;jsessionid=88F3973B9FD7A9D6FA007AF65958EAA8.route04?articleId=4115720
[ Supreme court on 20-11-2012 pulls up Tamilnadu on lethargic disaster planning and calls for action]
http://www.aerb.gov.in/t/sj/Siting.pdf [Impact Zone of 30km.as cited in page-20 of IAEA Guide]
http://thebulletin.org/web-edition/features/china-responds-to-fukushima [China suspends reactors work]
COMPARITIVE EMISSIONS FROM TMI,CHERNOBYL,FUKUSHIMA DURING ACCIDENTS
http://www.ccnr.org/rasmussen.html
(WASH-1400 Nuclear Safety report with extensive detailed discussion)
http://www.southernstudies.org/2009/04/post-4.html [TMI releases]
For example, the official story is that the TMI incident released only 13 to 17 curies of dangerous iodine into the outside environment, a tiny fraction of the 13 million curies of less dangerous radioactive gases officials say were released, primarily xenon. Such a number would seem small compared with, for example, the 1986 nuclear accident at Chernobyl, which released anywhere from 13 million to 40 million curies of iodine and is linked to 50,000 cases of thyroid cancer, according to World Health Organization estimates
Is a District collector competent to plan and execute Nuclear Emergency Preparedness Plan?
[ comparitive costs of Nuclear,coal,Gas,wind Energies]
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheet/ccc?key=0AonYZs4MzlZbdFc0cVRMVDR5c1ZmeC1lR2hac0xjMXc&hl=en#gid=1
( 36 nuclear incidents and accidents reported in various countries by IAEA )
(Accidents reported by Green Peace since 1951)
(Protective actions during a nuclear accident,USA)
http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:Y0-hR3nU9eEJ:128.173.204.63/courses/cee4674/cee4674_pub/aircraft_classifications10.pdf+&cd=4&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=in [ kudankulam fails as it withstands only Cessna & Learjets and not Boeings& Air Buses]
http://tribune.com.pk/story/478296/why-i-said-90-per-cent-of-indians-are-fools/ {Idiots-Indians?]}
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/05/120522134942.htm (Max Planck)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/nuregs/staff/sr1150/v1/sr1150v1-intro-and-part-1.pdf
[Explosion caases ocf FI VE rea ctors i n USA for disaster managemwent examples]
http://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyNET.exe/9100AE95.txt?ZyActionD=ZyDocument&Client=EPA&Index=1981%20Thru%201985&Docs=&Query=&Time=&EndTime=&SearchMethod=1&TocRestrict=n&Toc=&TocEntry=&QField=&QFieldYear=&QFieldMonth=&QFieldDay=&UseQField=&IntQFieldOp=0&ExtQFieldOp=0&XmlQuery=&File=D%3A\ZYFILES\INDEX%20DATA\81THRU85\TXT\00000016\9100AE95.txt&User=ANONYMOUS&Password=anonymous&SortMethod=h|-&MaximumDocuments=1&FuzzyDegree=0&ImageQuality=r75g8/r75g8/x150y150g16/i425&Display=p|f&DefSeekPage=x&SearchBack=ZyActionL&Back=ZyActionS&BackDesc=Results%20page&MaximumPages=1&ZyEntry=1
[AIR pollutioin Modelling Text Book ,lume Rise]
http://www.thehindu.com/multimedia/archive/00948/Concept_of_Defense-_948126a.pdf [Figure]
www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/.../Judgement-Kudankulam%20..
[Madras High Court Orders on Kudankulam Reactors,suggestin 30km.evacuation]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Japanese_reaction_to_Fukushima_Daiichi_nuclear_disaster
(Compensation to Victims by Japan is Rs.3 lakh crores + Evacuation events)
http://www.aerb.gov.in/T/PUBLICATIONS/CODESGUIDES/sg-s-1.pdf
(AERB on Radiation fall-out Modelling)
http://www.fema.gov/sites/default/files/orig/fema_pdfs/pdf/about/divisions/thd/rep_pg_manual_interim [ FEMA DISASTER panning ,EXCELLENT]
http://www.utsandiego.com/news/2011/apr/12/mock-nuclear-accident-drill-held-in-california/
[ MOCK DRILL FOR NUCLEAR DISASTER IN CALIFORNIA]
http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2149154/Catastrophic-nuclear-reactor-meltdowns-like-Chernobyl-Fukushima-happen-20-years-scientists-warn.html [probability of accidents]
http://news.blogs.cnn.com/2012/08/21/record-radiation-found-in-fish-near-fukushima-plant/
http://www.jfa.maff.go.jp/e/inspection/index.html (Fisheries pollution, Fukushima)
http://www.thehindu.com/news/states/tamil-nadu/sc-asks-tn-govt-to-submit-safety-plan-for-kknp/article4115720.ece [ SC asks Tamilnadu for Disaster plan Details of Mock-Drill]
http://www.shodor.org/cgi-bin/cascgi/plume.pl ]Gaussian model soft=ware for work]
http://ec.europa.eu/energy/nuclear/radioprotection/doc/studies/emergency_planning_en.pdf
(Source terms, DNA break, health impacts + EXCELLENT ARTICLE)
http://www.aerb.gov.in/T/PUBLICATIONS/CODESGUIDES/sg-s-1.pdf
(AERB guidelines for air pollution levels upto 30km, see item-1.3 under Introduction)
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/INES-2009_web.pdf- (Working Model for Event category)
http://www.thehindu.com/forum/comment.do;jsessionid=88F3973B9FD7A9D6FA007AF65958EAA8.route04?articleId=4115720
[ Supreme court on 20-11-2012 pulls up Tamilnadu on lethargic disaster planning and calls for action]
http://www.aerb.gov.in/t/sj/Siting.pdf [Impact Zone of 30km.as cited in page-20 of IAEA Guide]
http://thebulletin.org/web-edition/features/china-responds-to-fukushima [China suspends reactors work]
COMPARITIVE EMISSIONS FROM TMI,CHERNOBYL,FUKUSHIMA DURING ACCIDENTS
The French radiation protection authority, Institut de
Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire (IRSN), estimates the radioactive
releases of iodine-131 in Japan had reached about 2.4 million curies by March
22, 2011. That is about 160,000 times the best estimate of the amount released
during the TMI accident in Pennsylvania (15 curies) and about 140,000 times the
maximum estimate of 17 curies. It is about 10 percent of the estimated amount
released during the Chernobyl accident, according to the IRSN. Combined
cesium-134 (half-life: about 2 years) and cesium-137 (half life: about 30
years) releases from Fukushima are estimated at about half-a-million curies,
about 10 percent of estimated Chernobyl cesium releases. The TMI accident did
not emit measurable amounts of radioactive cesium, according to the
presidential commission that investigated the accident
Large quantities of water with
radioactive material were released into the containment building. The
containment building performed, as designed and radioactive releases to the atmosphere
were small. It resulting in the release of up to 370 PBq (1 PBq = 1015 Bq) of
radioactive noble gases, and about 0.55 TBq (1 TBq = 1012 Bq) of 131I. The average
radiation dose to people living within ten miles (16 km) of the plant was 0.08
mSv, and no more than 1 mSv to any single individual. Based on these emission
figures, scientific publications on the health effects of the fallout estimated
one or two additional cancer deaths in the 16 km area around nuclear power
plant.
Major
releases of radionuclides from the Chernobyl reactor continued for ten days
following the explosion on April 26. These included radioactive gases,
condensed aerosols, and fuel particles. The total release of radioactive
material was about 14 EBq (1 EBq = 1018 Bq),
including 1.8 EBq of 131I, 0.085 EBq of 137Cs, 0.01 EBq of 90Sr
and 0.003 EBq of plutonium isotopes. Radioactive noble gases contributed about
50% of the total activity released (Table 2).
The total discharge amounts
from the reactors of Fukushima-1 NPP were estimated as 0.16 EBq for 131I and 0.015
EBq 137Cs.
Approximately
7800 emergency workers were exposed to about 7.7 mSv on average. Thirty people
were recorded as receiving doses over 100 mS
http://www.ccnr.org/rasmussen.html
(WASH-1400 Nuclear Safety report with extensive detailed discussion)
http://www.southernstudies.org/2009/04/post-4.html [TMI releases]
For example, the official story is that the TMI incident released only 13 to 17 curies of dangerous iodine into the outside environment, a tiny fraction of the 13 million curies of less dangerous radioactive gases officials say were released, primarily xenon. Such a number would seem small compared with, for example, the 1986 nuclear accident at Chernobyl, which released anywhere from 13 million to 40 million curies of iodine and is linked to 50,000 cases of thyroid cancer, according to World Health Organization estimates
Is a District collector competent to plan and execute Nuclear Emergency Preparedness Plan?
In accordance with statutory requirements, it is the local District Administration which is responsible for drawing up and testing the Off Site Emergency Plans. NPCIL has co-ordinated with all concerned District Administration to enable them to draw up comprehensive Off Site Emergency Plans for each power station. It may be mentioned that the AERB does not permit any nuclear power station to be commissioned unless and until, such plans for all types of Emergencies are in place well before the commissioning date.
http://www.nytimes.com/2012/03/04/world/asia/japans-premier-says-government-shares-blame-for-fukushima-disaster.html {NODA says Nuclear safety is a Myth\
The accident at the Fukushima plant is likely to have released about 15 percent of the radiation released at Chernobyl in 1986, Japan's Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency has estimated.
But that is still more than seven times the amount of radiation produced by Three Mile Island accident in the United States in 1979, and experts have estimated
Japan's decontamination efforts could cost as much as 10 trillion yen ($130 billion).
http://www.reuters.com/article/2011/08/27/us-japan-nuclear-uninhabitable-idUSTRE77Q17U20110827
http://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/phys_agents/ionizing.html (Conversion units, Cu, Rems, Sv)
http://www.dianuke.org/starting-koodankulam-reactor-without-sufficient-backup-water-would-be-fatal/ (Fuel disposal and good article)
http://www.radscihealth.org/rsh/Docs/Pollycove/MP-LF0901JNM.pdf [Low Dose,is it good?]
http://www.in.boell.org/web/113-779.html [PM told DAE to update Nuclear safety]
http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/cag-pulls-up-aerb-for-not-preparing-nuclear-safety-policy/article3808724.ece
[ CAG pulls up AERB for failure to develop Nuclear SAFETY POLICY ]
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/nuregs/staff/sr1150/v2/sr1150v2appb.pdf
(Surray Reactor accident, NUREG1150)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/cfr/part050/part050-appe.html
[USA on Emergency planning]]
http://www.pnas.org/content/97/1/103.full.pdf+html
( Low Radiation damages DNA and no safe limit)
http://hps.org/documents/IRSN_Fukushima_Report.pdf
(Fukushima accident scenarios with data)
http://www.irsn.fr/EN/news/Pages/201103_seism-in-japan.aspx
http://www.weatheronline.co.uk/weather/news/fukushima?LANG=en&VAR=irsnsum
(Animation for pollution spread due to Fukushima in air, and marine waters by IRSN, French Govt.,)
http://www.hpa.org.uk/Publications/Radiation/HPARPDSeriesReports/HpaRpd019/ [Routine daily Releases of Radio activity from a nuclear plant into air,water,soil etc.]
http://www.nytimes.com/2012/03/04/world/asia/japans-premier-says-government-shares-blame-for-fukushima-disaster.html {NODA says Nuclear safety is a Myth\
The accident at the Fukushima plant is likely to have released about 15 percent of the radiation released at Chernobyl in 1986, Japan's Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency has estimated.
But that is still more than seven times the amount of radiation produced by Three Mile Island accident in the United States in 1979, and experts have estimated
Japan's decontamination efforts could cost as much as 10 trillion yen ($130 billion).
http://www.reuters.com/article/2011/08/27/us-japan-nuclear-uninhabitable-idUSTRE77Q17U20110827
http://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/phys_agents/ionizing.html (Conversion units, Cu, Rems, Sv)
http://www.dianuke.org/starting-koodankulam-reactor-without-sufficient-backup-water-would-be-fatal/ (Fuel disposal and good article)
http://www.radscihealth.org/rsh/Docs/Pollycove/MP-LF0901JNM.pdf [Low Dose,is it good?]
http://www.in.boell.org/web/113-779.html [PM told DAE to update Nuclear safety]
WHY GERMAN CHANCELLOR CONFIRMED THAT NUCLEAR SAFETY IS A MYTH ?
The CDU-led government under Chancellor Angela Merkel made an
aboutface in their nuclear energy policy. In 2010 the Government had
just prolonged the retention period of nuclear power plants which were
scheduled to be phased out in 2021 by the nuclear phase-out plan of
2000. In light of the Fukushima disaster, the Government changed its
mind:
A physicist by training and a former environment minister, Merkel
understood what Fukushima meant. Germany has 17 reactors, providing 23
percent of the electrical power in the country and making it the sixth
largest nuclear electricity producer in the world. The eight oldest
reactors were taken off the grid within days of 3/11 and will not return
to operation. In record time, what once was the most pro-nuclear German
government in decades prepared comprehensive legislation to phase out
the remaining nine reactors by 2022 at the latest, starting in 2015. In
June, parliament overwhelmingly passed the law (513 in favor, 79
against, 8 abstentions).[75]
http://www.thehindu.com/opinion/editorial/a-sure-recipe-for-disaster/article3836701.ece
http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/cag-pulls-up-aerb-for-not-preparing-nuclear-safety-policy/article3808724.ece
[ CAG pulls up AERB for failure to develop Nuclear SAFETY POLICY ]
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/nuregs/staff/sr1150/v2/sr1150v2appb.pdf
(Surray Reactor accident, NUREG1150)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/cfr/part050/part050-appe.html
[USA on Emergency planning]]
http://www.pnas.org/content/97/1/103.full.pdf+html
( Low Radiation damages DNA and no safe limit)
http://hps.org/documents/IRSN_Fukushima_Report.pdf
(Fukushima accident scenarios with data)
http://www.irsn.fr/EN/news/Pages/201103_seism-in-japan.aspx
http://www.weatheronline.co.uk/weather/news/fukushima?LANG=en&VAR=irsnsum
(Animation for pollution spread due to Fukushima in air, and marine waters by IRSN, French Govt.,)
http://www.hpa.org.uk/Publications/Radiation/HPARPDSeriesReports/HpaRpd019/ [Routine daily Releases of Radio activity from a nuclear plant into air,water,soil etc.]
[The exposure measured in air. for the deposit of 1 joule per kilogram has the unit of 1 gray
(Gy).
]For 1 MeV energy gamma rays, an exposure of 1 röntgen in air produces a dose of about 0.01 gray (1 centigray, cGy) in water or surface tissue. Because of shielding by the tissue surrounding the bones, the bone marrow only receives about 0.67 cGy when the air exposure is 1 röntgen and the surface skin dose is 1 cGy.]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/pdf/SER_KKNPP_3_6_21jun2012.pdf (No Emergency Plan details?)
http://www.nirs.org/reactorwatch/emergency/epzresolution.pdf [Demand to expand EPZ to 100 km]
http://www.ucsusa.org/assets/documents/nuclear_power/nuc_risk.pdf [ Fukushima lessons]
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/commission/slides/2012/20120911/09-06-12-comments-pilgrim-watch.pdf [NGO,pilgrim watch on Fukushima lessons for USNRC]
http://www.iaea.org/newscenter/focus/fukushima/japan-report2/ [ fukushima Lessons by japan]
No nuclear power plant is and never be 100 % safe. Disaster that happened in Fukushima last year just reminded this uncompromising fact.
http://www.energyinslovakia.sk/2012/10/michal-hudec-final-report-on-stress.html
http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/f9961e7c-fe3e-11e1-8228-00144feabdc0.html#axzz26YiAFf9H
[Japan decided to phase out nuclear plants by 2040 on 14-9-2012 due to public pressure]]
http://www.thehindu.com/opinion/editorial/article3836701.ece
(Hindu editorial on AERB, a prescription for disaster)
http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/montreal/story/2012/10/03/montreal-gentilly-2-shutdown-cost-hydro-quebec.html [Decommissioning a Reactor,canada,costs $2.0 billion=Rs.10,000CRORES]
http://www.beyondnuclear.org/storage/documents/Tritiumbasicinfofinal.pdf
[Unavoidable Radio active poisonous pollutants from every Nuclear plant in the world]
http://www-ns.iaea.org/downloads/ni/training/TCS-15_web.pdf [IAEA safety norms]
http://www.nuclearfaq.ca/ReviewofGreenpeacereport_Final.pdf [Tritium pollution from Reactors]
http://iicph.org/files/health-effects-of-tritium.pdf [Health impacts of Tritium pollution on life]
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/shows/reaction/readings/search.html
(Perow's article on reasons for impossibility of nuclear safety)
http://beyondnuclear.squarespace.com/storage/routine_releases_tritium_and_noble_gases_jan.2009.pdf
[Compulsary Tritium,Xenon,Crypton pollutants discharges into environment from reactors]
http://www-ns.iaea.org/downloads/rw/meetings/environ-consequences-report-wm-08.05.pdf
(CONCENTRATIONS OF RADIOACTIVE POLLUTANTS FROM CHERNOBYL ACCIDENT)
http://www.nks.org/scripts/getdocument.php?file=111010111119412
(EIA for a nuclear plant accident in Norway, 296 page report)
http://www.nks.org/scripts/getdocument.php?file=111010111119314
(nuclear reactor explosion scenario in Norway, 70 pages report)
http://www.beyondnuclear.org/fact-sheets/ [Tritium pollution and fisheries]
http://www.rpe.org.in/temp/RadiatProtEnviron34117-1574386_002614.pdf
[ Summary of National Disaster Management report on Indian reactor accidents]
http://www.bellona.org/articles/articles_2011/japan_revamp
[Emergency Evacuation in Russia is only 3 km while Japan revised it to 50 km.]
http://www.bellona.org/english_import_area/international/russia/nuke_industry/20156
[Bellona reports on risks of Russian reactors as reported in Russia for VVER Units]
http://www.rferl.org/content/russia_nuclear_power_plants_unsafe_criticisms/2342630.html#relatedInfoContainer [Safety of Russian Reactors questioned by experts]
http://www.nirs.org/reactorwatch/aging/nrdcaccidentip1011.pdf
[Indiana Point Reactor Accident scenario compared with Fukushima and Chernobyl]
http://www.radstats.org.uk/no029/speed.pdf [Reactor safety studies,unbewlievable]
http://www.fepc.or.jp/library/pamphlet/zumenshu/pdf/all_english.pdf
[ Energy sources for different countries in the world +disposal of Nuclear wastes]
http://ukrainianweek.com/Columns/50/46030 [Safety is an impossibility in Rusasian units]
http://www10.antenna.nl/wise/index.html?http://www10.antenna.nl/wise/terrorism/112001vver.html
[ Unsafe VVER-1000 MW Reactors i n Russia]
http://www.decomatom.org/node [Russian reactors in bad shape]
http://ajw.asahi.com/article/0311disaster/fukushima/AJ201206070071
(Nuclear Safety commission,Japan widened emergency evacuation zone upto 30 km)
]For 1 MeV energy gamma rays, an exposure of 1 röntgen in air produces a dose of about 0.01 gray (1 centigray, cGy) in water or surface tissue. Because of shielding by the tissue surrounding the bones, the bone marrow only receives about 0.67 cGy when the air exposure is 1 röntgen and the surface skin dose is 1 cGy.]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/pdf/SER_KKNPP_3_6_21jun2012.pdf (No Emergency Plan details?)
http://www.nirs.org/reactorwatch/emergency/epzresolution.pdf [Demand to expand EPZ to 100 km]
http://www.ucsusa.org/assets/documents/nuclear_power/nuc_risk.pdf [ Fukushima lessons]
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/commission/slides/2012/20120911/09-06-12-comments-pilgrim-watch.pdf [NGO,pilgrim watch on Fukushima lessons for USNRC]
http://www.iaea.org/newscenter/focus/fukushima/japan-report2/ [ fukushima Lessons by japan]
No nuclear power plant is and never be 100 % safe. Disaster that happened in Fukushima last year just reminded this uncompromising fact.
http://www.energyinslovakia.sk/2012/10/michal-hudec-final-report-on-stress.html
http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/f9961e7c-fe3e-11e1-8228-00144feabdc0.html#axzz26YiAFf9H
[Japan decided to phase out nuclear plants by 2040 on 14-9-2012 due to public pressure]]
http://www.thehindu.com/opinion/editorial/article3836701.ece
(Hindu editorial on AERB, a prescription for disaster)
http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/montreal/story/2012/10/03/montreal-gentilly-2-shutdown-cost-hydro-quebec.html [Decommissioning a Reactor,canada,costs $2.0 billion=Rs.10,000CRORES]
http://www.beyondnuclear.org/storage/documents/Tritiumbasicinfofinal.pdf
[Unavoidable Radio active poisonous pollutants from every Nuclear plant in the world]
http://www-ns.iaea.org/downloads/ni/training/TCS-15_web.pdf [IAEA safety norms]
http://www.nuclearfaq.ca/ReviewofGreenpeacereport_Final.pdf [Tritium pollution from Reactors]
http://iicph.org/files/health-effects-of-tritium.pdf [Health impacts of Tritium pollution on life]
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/shows/reaction/readings/search.html
(Perow's article on reasons for impossibility of nuclear safety)
http://beyondnuclear.squarespace.com/storage/routine_releases_tritium_and_noble_gases_jan.2009.pdf
[Compulsary Tritium,Xenon,Crypton pollutants discharges into environment from reactors]
http://www-ns.iaea.org/downloads/rw/meetings/environ-consequences-report-wm-08.05.pdf
(CONCENTRATIONS OF RADIOACTIVE POLLUTANTS FROM CHERNOBYL ACCIDENT)
http://www.nks.org/scripts/getdocument.php?file=111010111119412
(EIA for a nuclear plant accident in Norway, 296 page report)
http://www.nks.org/scripts/getdocument.php?file=111010111119314
(nuclear reactor explosion scenario in Norway, 70 pages report)
http://www.beyondnuclear.org/fact-sheets/ [Tritium pollution and fisheries]
http://www.rpe.org.in/temp/RadiatProtEnviron34117-1574386_002614.pdf
[ Summary of National Disaster Management report on Indian reactor accidents]
http://www.bellona.org/articles/articles_2011/japan_revamp
[Emergency Evacuation in Russia is only 3 km while Japan revised it to 50 km.]
http://www.bellona.org/english_import_area/international/russia/nuke_industry/20156
[Bellona reports on risks of Russian reactors as reported in Russia for VVER Units]
http://www.rferl.org/content/russia_nuclear_power_plants_unsafe_criticisms/2342630.html#relatedInfoContainer [Safety of Russian Reactors questioned by experts]
http://www.nirs.org/reactorwatch/aging/nrdcaccidentip1011.pdf
[Indiana Point Reactor Accident scenario compared with Fukushima and Chernobyl]
http://www.radstats.org.uk/no029/speed.pdf [Reactor safety studies,unbewlievable]
http://www.fepc.or.jp/library/pamphlet/zumenshu/pdf/all_english.pdf
[ Energy sources for different countries in the world +disposal of Nuclear wastes]
http://ukrainianweek.com/Columns/50/46030 [Safety is an impossibility in Rusasian units]
http://www10.antenna.nl/wise/index.html?http://www10.antenna.nl/wise/terrorism/112001vver.html
[ Unsafe VVER-1000 MW Reactors i n Russia]
http://www.decomatom.org/node [Russian reactors in bad shape]
http://www.bellona.org/subjects/Power_reactors_in_the_ex-Soviet_republics [Reactors in USSR]
http://www.japantimes.co.jp/text/nn20110927f1.html [Nuclear proponents oppose safer energies]
(Three Mile Island accident emergency evacuation done upto 32 km)
http://ajw.asahi.com/article/0311disaster/fukushima/AJ201206070071
(Nuclear Safety commission,Japan widened emergency evacuation zone upto 30 km)
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/02688867.1986.9726562 [size well,30km.zone]
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/Pub1467_web.pdf [IAEA latest standards for EAP]
http://ec.europa.eu/energy/nuclear/radioprotection/doc/studies/emergency_planning_en.pdf (pages 44 to 50)
(While mechanical reactor safety may be possible public safety of the reactor is impossible)
http://archive.greenpeace.org/comms/97/nuclear/reactor/russiaenergyfull.html
[ Risky russian Reactors]
http://en.rian.ru/natural/20110708/165081125.html [a storm shuts down a Russian reactor]
http://www.outlookindia.com/article.aspx?203718 [ kudankulam plant risky,1997 report]
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9gERUtbtkRc&feature=endscreen&NR=1
[Animation on Binding Energy between atoms thrown out by fission]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/pdf/news_28sep2011_02.pdf (
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/Pub1467_web.pdf [IAEA latest standards for EAP]
http://ec.europa.eu/energy/nuclear/radioprotection/doc/studies/emergency_planning_en.pdf (pages 44 to 50)
(While mechanical reactor safety may be possible public safety of the reactor is impossible)
http://archive.greenpeace.org/comms/97/nuclear/reactor/russiaenergyfull.html
[ Risky russian Reactors]
http://en.rian.ru/natural/20110708/165081125.html [a storm shuts down a Russian reactor]
http://www.outlookindia.com/article.aspx?203718 [ kudankulam plant risky,1997 report]
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9gERUtbtkRc&feature=endscreen&NR=1
[Animation on Binding Energy between atoms thrown out by fission]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/pdf/news_28sep2011_02.pdf (
NPCIL Experts, evacuation in exclusion and not sterilized zone of 5km
[AERB Limitas of radiation exposure:public;1.0 mSv/year;Workers;20 mSv/year]
http://www.aerb.gov.in/T/PUBLICATIONS/CODESGUIDES/S-8.PDF (AERB evacuation 30km)
http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/12/4245/2012/acp-12-4245-2012.pdf [Accidental Radio-activity
90%crosses 50km,and 50%crosses 1000km.from the reactor explosion site]
90 5http://nidm.gov.in/PDF/guidelines/nuclear_radiological_emergencies.pdf [NDMA,Accident scenario]
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/05/120522134942.htm [Nuclear accidents :one/decade]
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v440/n7087/full/440984a.html [ Nuclear very costly]
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2796747/ [Nuclear safety standards,NPCIL data]
http://pbadupws.nrc.gov/docs/ML1202/ML12026A470.pdf [Excellent emergency plan ning zones]
http://www.laka.org/docu/boeken/pdf/6-01-3-90-48.pdf [Reactor accident emissions, in 5countyries]
http://www.jstor.org/discover/10.2307/2398122?uid=3738256&uid=2&uid=4&sid=56188501953
http://www.hse.gov.uk/nuclear/tolerability.pdf [ Size Well Reactor Enquiryies on safety aspects]
http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/article3407658.ece?css=print [SC comes in,if Govt. violates Law of the Land,12-5-2012,mining cases]
http://www.japantoday.com/category/national/view/storn-briefly-halts-cooling-system-for-fuel-pool-at-onagawa-nuclear-power-plant [ a storm hkit a reactor safety issue]
http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/111111111/2756/1/reqno_jrc43311_final%20version%5B2%5D.pdf [EPzones for U.s.,hungary,IAEA view]
http://www.dhses.ny.gov/oem/radiological/documents/Procedure-K.3.11.pdf
[Like New York state,Tamilnadu has to bear the heaviest costs to plan for Accident Rmediation measures that costs Rs.4 lakhs crores due to kudankulam accidents in due course.Do Tamilians know about such hidden costs which pass on as penalties over shoulders of Tamilian people now and in future also]
http://nuclearsafety.gc.ca/eng/lawsregs/regulatorydocuments/published/html/rd346/#P204_18706
[ Kudankulam reactor site was not evaluated for safety as per standards followed in canada etc.,]
https://netfiles.uiuc.edu/mragheb/www/NPRE%20402%20ME%20405%20Nuclear%20Power%20Engineering/Pressurized%20Water%20Reactors.pdf [Dimensions of reactor core components]
http://www.epsc.org/data/files/PRISM/frankfurt_8kletz.pdf [Human errors cause reactor explosion]
https://netfiles.uiuc.edu/mragheb/www/NPRE%20457%20CSE%20462%20Safety%20Analysis%20of%20Nuclear%20Reactor%20Systems/Containment%20Structures.pdf (Figures of reactors and parts, Fig-25)
http://www.pibchennai.gov.in/karuvoolam/Releases%202012/January%202012/KKNPP31.01.2012.pdf (GOI and NGO joint meeting on Kudankulam safety aspects)
http://www.solarcellcentral.com/nuclear_page.html (Details of nuclear plant and decommissioning)
http://napm-india.org/node/233
[Medha Patkar against nuc lear plants in India]
http://ec.europa.eu/energy/nuclear/radiation_protection/doc/publication/153.pdf
[Radiatio data from European Reactors into Air and water ]
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/06/25/world/asia/25myth.html?pagewanted=all
(New York times gives how nuclear lobby propagates to brainwash people on nuclear safety)
http://www.hpa.org.uk/webc/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1197382221858 [Tritium impacts on cells]
http://www.abpischools.org.uk/page/modules/genome/dna2.cfm?coSiteNavigation_allTopic=1
(DNA ANIMATION)
http://www.japantimes.co.jp/text/eo20120418a4.html [M.I.T. Ph.D.on Fukushima Accident]
http://pr.bbt757.com/eng/ [Fukushima Real story b y A Ph.D.,]
http://doh.wa.gov/ehp/hanford/publications/overview/radioactivity.html#VC2cc5
[Routine Releases of Radio izsotopes into air and columba water by Man ,Reactors]
http://www.yomiuri.co.jp/dy/national/T120416004238.htm
(Japan decides on 17-4-2012 to close down all the reactors)
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/P082_scr.pdf
(Nuclear safety implies general safety, radiation protection, technical safety, safety culture, responsibilities are the plant management and also an effective regulatory control and verification through eternal vigilence)
http://tshivajirao.blogspot.in/2011/10/kudankulam-nuclear-plant-explosion.html (explosion scenario)
https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&q=cache:GWeH1FZeXroJ:www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/eprmedt/Day_2/Day_2-6b.pps+&hl=en&gl=in&pid=bl&srcid=ADGEESgh-te4fzC_VQiS6mxLn1iEdKDJ2esfrvMflI3E6q7pUqX-yluMrt3YQ4d9kTTolnEUEaSeYKci3HR4bh_5yAEVvMBsyGEx6nsh1ADEwzSKriG4zQ7l0m10nu5qwA_zPcvhbRff&sig=AHIEtbTxtmqYCD0myRVjEKC6f9plVropwg&pli=1
www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/.../Day.../Day_2-6a.pps [PPT on Radiation Breaks]
http://nuclearinfo.net/Nuclearpower/TheRisksOfNuclearPower [No safe Limit of radiation]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_repair [Repair of Double strand Breaks in DNA]
http://www.iaea.org/Publications/Booklets/RadPeopleEnv/pdf/radiation_low.pdf [IAEA Guide]
http://www.elibrary.dep.state.pa.us/dsweb/Get/Document-81206/2910-FS-DEP4059.pdf [Tritium risks]
http://www.iem-inc.com/toolspa.html [Relative Energies of radio-nucleids]
http://www-ns.iaea.org/training/rw/radiorweb/chap1/chap15.htm [animations,radiation ionisation effects]
http://www-ns.iaea.org/training/rw/radiorweb/chap1/index.htm
(Cell Ionisation, DNA damage by ionisation)
http://www.cyberphysics.co.uk/topics/radioact/Radio/Glossary.htm [Glossary of Radiation]
http://www.rerf.jp/radefx/basickno_e/radcell.htm
(Linear Energy Transfer by high LET and Low LET radioactivity)
http://www.abelard.org/briefings/ionising-radiation.php#x-rays
(Background radiation due to less harmful radioactivity is magnified by Nuclear plants)
http://www.ieer.org/ensec/no-3/puhealth.html
(Plutonium which is in traces in nature is magnified by weapons and reactors)
http://www.abelard.org/briefings/ionising-radiation.php#background_radiation [U-238 safer,units]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/main/ConstructionDetail.aspx?ReactorID=77 [status , kudankulam,NPCIL]
http://www.barc.ernet.in/egreport.pdf [GOI Expert Group on EIA report,kudankulam, Dec.2011]
http://pibmumbai.gov.in/English/PDF/E2012_FR39.PDF [Facts on Reactors,Hot Run,30-6-2011]
http://www.photobiology.com/educational/len/part2.htm (Ionisation Energy)
http://www.ratical.org/radiation/CNR/NoSafeThresh.html [No Safe Low Dose of radiation,Gofman]
http://www.ratical.org/radiation/CNR/FreeRadFallacy.html [free radicals,ionisation,Goffman]
http://www.hiroshimasyndrome.com/radiation-the-no-safe-level-myth.html [Hormetic dose,50 rems]
http://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/phys_agents/ionizing.html [Radiation ,conversion Units]
http://www.scchealth.org/docs/ems/docs/prepare/tstorms.html [Hurricane,100 MPH ]
http://www.simplyinfo.org/?p=5628 [Storm damages Fukushima and oginawa reactors]
http://www.japantoday.com/category/national/view/storn-briefly-halts-cooling-system-for-fuel-pool-at-onagawa-nuclear-power-plant?utm_campaign=jt_newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_source=jt_newsletter_2012-04-04_PM
[ A storm caused 20 minutes failure of Cooling Systems in Japan even in 4 th.April,2012]
http://www.imd.gov.in/section/nhac/static/cyclone-history-bb.htm [Historical cyclones,dangerous]
http://au.news.yahoo.com/thewest/a/-/world/13345009/violent-storm-leaves-four-dead-in-japan/
[ 153km./hour winds of the storm cause Low Voltage,causing loss of cooling to Fuel storage]
http://www.guardian.co.uk/news/datablog/2011/mar/14/nuclear-power-plant-accidents-list-rank
[Nuclear Reactor Accidents in foreign countries indicate the Risks]
http://www.dianuke.org/accidents-at-nuclear-power-plants-in-india/
[ Many small scale accidents at Nuclear plants in India itself]
http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/fukushima_accident_inf129.html
[40 Km.evacuation ordered on 16-3-2011 Fukushima for Accident]
(G.O.270, Dt.27-12-2011)
http://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/nuke/R41694.pdf [Fukushima evacuation upto 40 km by japan]
http://www.nirs.org/reactorwatch/licensedtokill/LiscencedtoKill.pdf
http://www.irsn.fr/EN/news/Documents/IRSN_Fukushima-Accident_Impact-on-marine-environment-EN_20110404.pdf
(Radioactive pollution seriously damages marine life)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/nuregs/contract/cr6753/cr6753.pdf [Case studies of failures in reactors]
http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/12/4245/2012/acp-12-4245-2012.pdf [Accidental Radio-activity
90%crosses 50km,and 50%crosses 1000km.from the reactor explosion site]
90 5http://nidm.gov.in/PDF/guidelines/nuclear_radiological_emergencies.pdf [NDMA,Accident scenario]
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/05/120522134942.htm [Nuclear accidents :one/decade]
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v440/n7087/full/440984a.html [ Nuclear very costly]
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2796747/ [Nuclear safety standards,NPCIL data]
http://pbadupws.nrc.gov/docs/ML1202/ML12026A470.pdf [Excellent emergency plan ning zones]
http://www.laka.org/docu/boeken/pdf/6-01-3-90-48.pdf [Reactor accident emissions, in 5countyries]
http://www.jstor.org/discover/10.2307/2398122?uid=3738256&uid=2&uid=4&sid=56188501953
http://www.hse.gov.uk/nuclear/tolerability.pdf [ Size Well Reactor Enquiryies on safety aspects]
http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/article3407658.ece?css=print [SC comes in,if Govt. violates Law of the Land,12-5-2012,mining cases]
http://www.japantoday.com/category/national/view/storn-briefly-halts-cooling-system-for-fuel-pool-at-onagawa-nuclear-power-plant [ a storm hkit a reactor safety issue]
http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/111111111/2756/1/reqno_jrc43311_final%20version%5B2%5D.pdf [EPzones for U.s.,hungary,IAEA view]
http://www.dhses.ny.gov/oem/radiological/documents/Procedure-K.3.11.pdf
[Like New York state,Tamilnadu has to bear the heaviest costs to plan for Accident Rmediation measures that costs Rs.4 lakhs crores due to kudankulam accidents in due course.Do Tamilians know about such hidden costs which pass on as penalties over shoulders of Tamilian people now and in future also]
http://nuclearsafety.gc.ca/eng/lawsregs/regulatorydocuments/published/html/rd346/#P204_18706
[ Kudankulam reactor site was not evaluated for safety as per standards followed in canada etc.,]
https://netfiles.uiuc.edu/mragheb/www/NPRE%20402%20ME%20405%20Nuclear%20Power%20Engineering/Pressurized%20Water%20Reactors.pdf [Dimensions of reactor core components]
http://www.epsc.org/data/files/PRISM/frankfurt_8kletz.pdf [Human errors cause reactor explosion]
https://netfiles.uiuc.edu/mragheb/www/NPRE%20457%20CSE%20462%20Safety%20Analysis%20of%20Nuclear%20Reactor%20Systems/Containment%20Structures.pdf (Figures of reactors and parts, Fig-25)
http://www.pibchennai.gov.in/karuvoolam/Releases%202012/January%202012/KKNPP31.01.2012.pdf (GOI and NGO joint meeting on Kudankulam safety aspects)
http://www.solarcellcentral.com/nuclear_page.html (Details of nuclear plant and decommissioning)
http://napm-india.org/node/233
[Medha Patkar against nuc lear plants in India]
http://ec.europa.eu/energy/nuclear/radiation_protection/doc/publication/153.pdf
[Radiatio data from European Reactors into Air and water ]
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/06/25/world/asia/25myth.html?pagewanted=all
(New York times gives how nuclear lobby propagates to brainwash people on nuclear safety)
http://www.hpa.org.uk/webc/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1197382221858 [Tritium impacts on cells]
http://www.abpischools.org.uk/page/modules/genome/dna2.cfm?coSiteNavigation_allTopic=1
(DNA ANIMATION)
http://www.japantimes.co.jp/text/eo20120418a4.html [M.I.T. Ph.D.on Fukushima Accident]
http://pr.bbt757.com/eng/ [Fukushima Real story b y A Ph.D.,]
http://doh.wa.gov/ehp/hanford/publications/overview/radioactivity.html#VC2cc5
[Routine Releases of Radio izsotopes into air and columba water by Man ,Reactors]
http://www.yomiuri.co.jp/dy/national/T120416004238.htm
(Japan decides on 17-4-2012 to close down all the reactors)
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/P082_scr.pdf
(Nuclear safety implies general safety, radiation protection, technical safety, safety culture, responsibilities are the plant management and also an effective regulatory control and verification through eternal vigilence)
http://tshivajirao.blogspot.in/2011/10/kudankulam-nuclear-plant-explosion.html (explosion scenario)
https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&q=cache:GWeH1FZeXroJ:www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/eprmedt/Day_2/Day_2-6b.pps+&hl=en&gl=in&pid=bl&srcid=ADGEESgh-te4fzC_VQiS6mxLn1iEdKDJ2esfrvMflI3E6q7pUqX-yluMrt3YQ4d9kTTolnEUEaSeYKci3HR4bh_5yAEVvMBsyGEx6nsh1ADEwzSKriG4zQ7l0m10nu5qwA_zPcvhbRff&sig=AHIEtbTxtmqYCD0myRVjEKC6f9plVropwg&pli=1
www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/.../Day.../Day_2-6a.pps [PPT on Radiation Breaks]
http://nuclearinfo.net/Nuclearpower/TheRisksOfNuclearPower [No safe Limit of radiation]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_repair [Repair of Double strand Breaks in DNA]
http://www.iaea.org/Publications/Booklets/RadPeopleEnv/pdf/radiation_low.pdf [IAEA Guide]
http://www.elibrary.dep.state.pa.us/dsweb/Get/Document-81206/2910-FS-DEP4059.pdf [Tritium risks]
http://www.iem-inc.com/toolspa.html [Relative Energies of radio-nucleids]
http://www-ns.iaea.org/training/rw/radiorweb/chap1/chap15.htm [animations,radiation ionisation effects]
http://www-ns.iaea.org/training/rw/radiorweb/chap1/index.htm
(Cell Ionisation, DNA damage by ionisation)
http://www.cyberphysics.co.uk/topics/radioact/Radio/Glossary.htm [Glossary of Radiation]
http://www.rerf.jp/radefx/basickno_e/radcell.htm
(Linear Energy Transfer by high LET and Low LET radioactivity)
http://www.abelard.org/briefings/ionising-radiation.php#x-rays
(Background radiation due to less harmful radioactivity is magnified by Nuclear plants)
http://www.ieer.org/ensec/no-3/puhealth.html
(Plutonium which is in traces in nature is magnified by weapons and reactors)
http://www.abelard.org/briefings/ionising-radiation.php#background_radiation [U-238 safer,units]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/main/ConstructionDetail.aspx?ReactorID=77 [status , kudankulam,NPCIL]
http://www.barc.ernet.in/egreport.pdf [GOI Expert Group on EIA report,kudankulam, Dec.2011]
http://pibmumbai.gov.in/English/PDF/E2012_FR39.PDF [Facts on Reactors,Hot Run,30-6-2011]
http://www.photobiology.com/educational/len/part2.htm (Ionisation Energy)
http://www.ratical.org/radiation/CNR/NoSafeThresh.html [No Safe Low Dose of radiation,Gofman]
http://www.ratical.org/radiation/CNR/FreeRadFallacy.html [free radicals,ionisation,Goffman]
http://www.hiroshimasyndrome.com/radiation-the-no-safe-level-myth.html [Hormetic dose,50 rems]
http://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/phys_agents/ionizing.html [Radiation ,conversion Units]
http://www.scchealth.org/docs/ems/docs/prepare/tstorms.html [Hurricane,100 MPH ]
http://www.simplyinfo.org/?p=5628 [Storm damages Fukushima and oginawa reactors]
http://www.japantoday.com/category/national/view/storn-briefly-halts-cooling-system-for-fuel-pool-at-onagawa-nuclear-power-plant?utm_campaign=jt_newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_source=jt_newsletter_2012-04-04_PM
[ A storm caused 20 minutes failure of Cooling Systems in Japan even in 4 th.April,2012]
http://www.imd.gov.in/section/nhac/static/cyclone-history-bb.htm [Historical cyclones,dangerous]
http://au.news.yahoo.com/thewest/a/-/world/13345009/violent-storm-leaves-four-dead-in-japan/
[ 153km./hour winds of the storm cause Low Voltage,causing loss of cooling to Fuel storage]
http://www.guardian.co.uk/news/datablog/2011/mar/14/nuclear-power-plant-accidents-list-rank
[Nuclear Reactor Accidents in foreign countries indicate the Risks]
http://www.dianuke.org/accidents-at-nuclear-power-plants-in-india/
[ Many small scale accidents at Nuclear plants in India itself]
http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/fukushima_accident_inf129.html
[40 Km.evacuation ordered on 16-3-2011 Fukushima for Accident]
(G.O.270, Dt.27-12-2011)
http://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/nuke/R41694.pdf [Fukushima evacuation upto 40 km by japan]
http://www.nirs.org/reactorwatch/licensedtokill/LiscencedtoKill.pdf
(Killing fishes and marine life due to reactor effluents,
cheating by nuclear industry pages 101 and 104)
http://www.greenpeace.org/canada/Global/canada/report/2007/6/tritium-hazard-report-pollu.pdf
[Annual Tritium pollutants into air and water from Reactors and damaging impacts )
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Environmental_impact_of_nuclear_power#Radioactive_gases_and_effluents
http://e360.yale.edu/feature/radioactivity_in_the_ocean_diluted_but_far_from_harmless/2391/
http://e360.yale.edu/feature/radioactivity_in_the_ocean_diluted_but_far_from_harmless/2391/http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Environmental_impact_of_nuclear_power#Radioactive_gases_and_effluents
http://e360.yale.edu/feature/radioactivity_in_the_ocean_diluted_but_far_from_harmless/2391/
http://www.irsn.fr/EN/news/Documents/IRSN_Fukushima-Accident_Impact-on-marine-environment-EN_20110404.pdf
(Radioactive pollution seriously damages marine life)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/nuregs/contract/cr6753/cr6753.pdf [Case studies of failures in reactors]
http://www.ehow.com/list_7298588_causes-nuclear-power-plant-accidents_.html [Reaasons for accidents]
http://www.ib.cnea.gov.ar/~protrad/biblioteca/3Accidentes.pdf [ Reactor Accidents, 1947 to 1001
h
http://www.dianuke.org/nuclear-free-carbon-free-world-possible/ [Alternate energy sources]
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/06/25/world/asia/25myth.html?pagewanted=all
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/04/27/world/asia/27collusion.html?pagewan
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/05/31/world/asia/31japan.html?pagewanted=allted=all
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pilgrim_Nuclear_Generating_Station
http://www.ib.cnea.gov.ar/~protrad/biblioteca/3Accidentes.pdf [ Reactor Accidents, 1947 to 1001
h
http://www.dianuke.org/nuclear-free-carbon-free-world-possible/ [Alternate energy sources]
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/06/25/world/asia/25myth.html?pagewanted=all
[New York Times presents Money power for spreading lies on safety of Nuclear plants,inJapan
http://tshivajirao.blogspot.in/2011/10/kudankulam-nuclear-plant-explosion.html http://www.nytimes.com/2011/04/27/world/asia/27collusion.html?pagewan
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/05/31/world/asia/31japan.html?pagewanted=allted=all
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pilgrim_Nuclear_Generating_Station
http://www.nei.org/resourcesandstats/documentlibrary/safetyandsecurity/reports/special-report-on-the-nuclear-accident-at-the-fukushima-daiichi-nuclear-power-station
(Timeline of events leading to Fukushima accident, NewYork times)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timeline_of_the_Fukushima_I_nuclear_accidents%20
(Timeline of events for Fukushima disaster, Wikipedia)
http://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/nuke/R41694.pdf (Rs.4 lakh crores, Fukushima disaster)
http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~meshkati/humanfactors.html
(80% accidents due to human errors)
http://www.theepochtimes.com/n2/world/japanese-atomic-agency-exposes-nuclear-accident-in-beijing-184888.html
(Chinese expert says 80% of nuclear accidents due to human errors)
http://www.hss.doe.gov/sesa/corporatesafety/hpc/docs/Ch1_IntroHPI.pdf
(Inst. of Nuclear Power Organisation says 75% nuclear accidents due to human erros)
http://www.profilschager.com/page109855.html
(Inherent polaity of man and natureleads to unavoidable reactors accidents)
http://www.pibchennai.gov.in/karuvoolam/Releases%202012/January%202012/KKNPP31.01.2012.pdf%20http://www.nrc.gov/about-nrc/emerg-preparedness/faq.html#2b
][Preparedness include mock drills and evacuation to find feasibility]
[ Government of India Expert committee Report on kudankulam.2012-unscientific]
http://www.thehindu.com/news/states/tamil-nadu/article3009853.ece [make it Gas-based,Ramdoss]
http://www.law.cornell.edu/rules/fre/rule_702 [How Judges must evaluate Expert opinions
http://jurisonline.in/2011/03/case-comment-law-society-of-india-v-fertilisers-and-chemicals-travancore-air-1994-ker-308/ [Cochin PIL on Ammonia tank as a hazard,H.C.admitted case]
http://www.welcometoreason.com/jaybeam/index.php?action=welcomereason&type=140
[V.R.Krishna Iyer on infallibility of Judges on River-linking]
http://thinkprogress.org/romm/2012/03/11/440367/the-nukes-of-hazard-fukushima-nuclear-power-remains-too-costly-to-be-a-major-climate-solution/
[Nuclear Energy is becoming too costly and so alternate sources are a must ]
][Preparedness include mock drills and evacuation to find feasibility]
[ Government of India Expert committee Report on kudankulam.2012-unscientific]
http://www.thehindu.com/news/states/tamil-nadu/article3009853.ece [make it Gas-based,Ramdoss]
http://www.law.cornell.edu/rules/fre/rule_702 [How Judges must evaluate Expert opinions
http://jurisonline.in/2011/03/case-comment-law-society-of-india-v-fertilisers-and-chemicals-travancore-air-1994-ker-308/ [Cochin PIL on Ammonia tank as a hazard,H.C.admitted case]
http://www.welcometoreason.com/jaybeam/index.php?action=welcomereason&type=140
[V.R.Krishna Iyer on infallibility of Judges on River-linking]
http://thinkprogress.org/romm/2012/03/11/440367/the-nukes-of-hazard-fukushima-nuclear-power-remains-too-costly-to-be-a-major-climate-solution/
[Nuclear Energy is becoming too costly and so alternate sources are a must ]
http://fukushima.greenaction-japan.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/04/PSR_Statement_on_Fukushima_Children.pdf [No Min.safe Level of radiation]
http://forum.prisonplanet.com/index.php?action=printpage;topic=203687.0 [Low doses,OK?]
http://www.deccanherald.com/content/233489/world-doesnt-need-n-energy.html [Ban Nuclear]
http://pbadupws.nrc.gov/docs/ML1202/ML120250406.pdf [ USA,for accidents2012]
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/cfr/part050/part050-apps.html [0.1 g Quake,PGA]
http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2011/aug/24/east-coast-earthquake-nuclear-plants
[Earth Quake prone areas in USA and design factors for Nuclear plants]
http://forum.prisonplanet.com/index.php?action=printpage;topic=203687.0 [Low doses,OK?]
http://www.deccanherald.com/content/233489/world-doesnt-need-n-energy.html [Ban Nuclear]
http://pbadupws.nrc.gov/docs/ML1202/ML120250406.pdf [ USA,for accidents2012]
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/cfr/part050/part050-apps.html [0.1 g Quake,PGA]
http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2011/aug/24/east-coast-earthquake-nuclear-plants
[Earth Quake prone areas in USA and design factors for Nuclear plants]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fukushima_Daiichi_nuclear_disaster#cite_note-mdn.mainichi.jp-54
http://www.japantoday.com/category/politics/view/cozy-relations-continue-between-politicians-nuclear-industry?utm_campaign=jt_newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_source=jt_newsletter_2012-03-11_PM
[Retired officials employed by nuclear industry to avoid safety measures]
http://www.greenpeace.org/india/en/What-We-Do/Nuclear-Unsafe/Safety/Nuclear-accidents/Nuclear-accidents-in-India/Accidents-at-nuclear-power-plants/ (Nuclear accidents, India)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corruption_Perceptions_Index
(Corruption Index, INDIA- 95, JAPAN-14)
http://ec.europa.eu/energy/nuclear/radioprotection/doc/studies/emergency_planning_en.pdf (European manual on nuclear accidents and emergency responses)
http://www.vtt.fi/inf/pdf/publications/2000/P422.pdf [Human Failures,Reactor Safety,Ph.D]
http://www.gepr.org/en/contents/20120101-02/ Economics of Fukushima accident]
http://www.nsc.org.in/ANNEXES/3.2.4%20Risk%20assessment%20and%20vulnerability%20maps/Tsunami%20Survey%20Report_Kanniyakumari.pdf (Tsunami at Kanyakumari,10m height)
http://journals1.scholarsportal.info/details.xqy?uri=/0012821x/v76i3-4_t/350_hsncacziteio.xml (Chagos bank rdige fault zone7.2 earthquake)
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/meetings/PDFplus/2011/cn200/documentation/cn200_Final-Fukushima-Mission_Report.pdf [Defects in Fukushima,violations of IAEA guidelines on safety]
http://www.oecd-nea.org/nea-news/2011/29-2/nea-news-29-2-fukushima-e.pdf [Costs of Fukushima]
http://www.animatedsoftware.com/environm/no_nukes/nukelist1.htm
[Several Nuclear plants were closed down in USA on safety considerations]
http://caliban.sourceoecd.org/vl=76617349/cl=13/nw=1/rpsv/cgi-bin/fulltextew.pl?prpsv=/ij/oecdjournals/16091914/v3n1/s1/p1l.idx
http://caliban.sourceoecd.org/vl=76617349/cl=13/nw=1/rpsv/cgi-bin/fulltextew.pl?prpsv=/ij/oecdjournals/16091914/v3n1/s1/p1l.idx [cHERNOBYL CALCULATIONS]
[Modelling routine pollution Levels,see pages 59 to 68 what about explosion releases? ]
http://www-pub.iaea.org/mtcd/publications/pdf/pub1239_web.pdf
(20 years impacts of nuclear accident at Chernobyl)
[ Fukushima forces activists plead for extending Emergency safety Zones of Reactors to 100km]
http://www.atmos-chem-phys-discuss.net/11/31207/2011/acpd-11-31207-2011-print.pdf
(Nuclear accident in any country causes nuclear pollution impacts in many other countries also)
(Fukushima radiation levels show that emergency zones must be changed from 30km to 40km based on levels
http://pbadupws.nrc.gov/docs/ML1114/ML11140A147.pdf%20%20
(Indiana Point Reactir accident -Emergency Response)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/fact-sheets/funds-fs.html%20(Price Anderson Act)
(Nuclear reactor accident scenario in finland
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0qX-wdwGpKc&feature=related
[Radiation exposure to public is 0.1 mSv/year usually and 5mSv/year for accidents,sec.9]
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mR6ORWldp2g
http://www.nirs.org/reactorwatch/aging/nrdcaccidentip1011.pdf [Indiana Reactor Disaster planning]
http://www-pub.iaea.org/mtcd/publications/pdf/method2003_web.pdf
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/06/25/world/asia/25myth.html?pagewanted=all [safetyUndue advt,by Japan] ]
http://www.dianuke.org/report-of-the-central-governments-expert-committee-on-koodankulam/http://www.japantoday.com/category/politics/view/cozy-relations-continue-between-politicians-nuclear-industry?utm_campaign=jt_newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_source=jt_newsletter_2012-03-11_PM
[Retired officials employed by nuclear industry to avoid safety measures]
http://www.greenpeace.org/india/en/What-We-Do/Nuclear-Unsafe/Safety/Nuclear-accidents/Nuclear-accidents-in-India/Accidents-at-nuclear-power-plants/ (Nuclear accidents, India)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corruption_Perceptions_Index
(Corruption Index, INDIA- 95, JAPAN-14)
http://ec.europa.eu/energy/nuclear/radioprotection/doc/studies/emergency_planning_en.pdf (European manual on nuclear accidents and emergency responses)
http://www.vtt.fi/inf/pdf/publications/2000/P422.pdf [Human Failures,Reactor Safety,Ph.D]
http://www.gepr.org/en/contents/20120101-02/ Economics of Fukushima accident]
http://www.nsc.org.in/ANNEXES/3.2.4%20Risk%20assessment%20and%20vulnerability%20maps/Tsunami%20Survey%20Report_Kanniyakumari.pdf (Tsunami at Kanyakumari,10m height)
http://journals1.scholarsportal.info/details.xqy?uri=/0012821x/v76i3-4_t/350_hsncacziteio.xml (Chagos bank rdige fault zone7.2 earthquake)
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/meetings/PDFplus/2011/cn200/documentation/cn200_Final-Fukushima-Mission_Report.pdf [Defects in Fukushima,violations of IAEA guidelines on safety]
http://www.oecd-nea.org/nea-news/2011/29-2/nea-news-29-2-fukushima-e.pdf [Costs of Fukushima]
http://www.animatedsoftware.com/environm/no_nukes/nukelist1.htm
[Several Nuclear plants were closed down in USA on safety considerations]
http://caliban.sourceoecd.org/vl=76617349/cl=13/nw=1/rpsv/cgi-bin/fulltextew.pl?prpsv=/ij/oecdjournals/16091914/v3n1/s1/p1l.idx
http://caliban.sourceoecd.org/vl=76617349/cl=13/nw=1/rpsv/cgi-bin/fulltextew.pl?prpsv=/ij/oecdjournals/16091914/v3n1/s1/p1l.idx [cHERNOBYL CALCULATIONS]
[Modelling routine pollution Levels,see pages 59 to 68 what about explosion releases? ]
http://www-pub.iaea.org/mtcd/publications/pdf/pub1239_web.pdf
(20 years impacts of nuclear accident at Chernobyl)
[Pilgrim Nuclear power plant,USA]
[Hazards of Pilgrim Nuclear plant]
http://www.timesunion.com/local/article/Coalition-Expand-nuclear-safety-zones-3334639.php[ Fukushima forces activists plead for extending Emergency safety Zones of Reactors to 100km]
http://www.atmos-chem-phys-discuss.net/11/31207/2011/acpd-11-31207-2011-print.pdf
(Nuclear accident in any country causes nuclear pollution impacts in many other countries also)
(Fukushima radiation levels show that emergency zones must be changed from 30km to 40km based on levels
http://pbadupws.nrc.gov/docs/ML1114/ML11140A147.pdf%20%20
(Indiana Point Reactir accident -Emergency Response)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/fact-sheets/funds-fs.html%20(Price Anderson Act)
(Nuclear reactor accident scenario in finland
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0qX-wdwGpKc&feature=related
[Radiation exposure to public is 0.1 mSv/year usually and 5mSv/year for accidents,sec.9]
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mR6ORWldp2g
http://www.nirs.org/reactorwatch/aging/nrdcaccidentip1011.pdf [Indiana Reactor Disaster planning]
http://www-pub.iaea.org/mtcd/publications/pdf/method2003_web.pdf
http://www.wittassociates.com/assets/249/Indian_Point_NYReport.pdf [Examples of Disasters,USA for Emergency planning as per NRC norms to compare with kudankulam]
...http://www.beyondnuclear.org/storage/emergency-planning/soarca/ep_soarca_ML12026A470.pdf
[US NRC publication on Accident scenario and impacts on health and other matters,2012]
http://www.nrc.gov/about-nrc/regulatory/research/soar/faqs.html [ public doubts on safety,USNRC]
http://pbadupws.nrc.gov/docs/ML1202/ML120250406.pdf [Accident scenario,NRC,USA]http://nidm.gov.in/PDF/guidelines/nuclear_radiological_emergencies.pdf
[ NDMA Guidelines on Nuclear Emergency preparedness plan] for Indian reactors ]
http://www.greenpeace.org/international/en/campaigns/nuclear/safety/ [Fukushima extends Zones]
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-13408055 ]Fukushima 30km.zone+$ 100 bn.costs Rs.5 lakh crores]
http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/article2615375.ece [Biggest lies of AEC officials]
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/health-12722435 [Fukushima ,health impacts]
http://science.howstuffworks.com/inside-nuclear-power-plant-pictures.htm
[Information on the Working of a Nuclear Plant with Figures]
http://www.iaea.org/Publications/Magazines/Bulletin/Bull254/25402043036.pdf
[IAEA study indicates that 60% Core Melt Downs occur due to Human failures]
http://www.rediff.com/news/column/india-corruption-nuclear-safety/20110318.htm [corrupt Deals?]
http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/fukushima_accident_inf129.html [Fu,kushima accident impacts]
http://www.nature.com/news/2011/110421/full/472400a.html [Reactors,people at Risk]
http://www.info.gov.za/view/DownloadFileAction?id=124577 [South Africa Reactors-Disasters]
http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/CFR-2011-title10-vol1/pdf/CFR-2011-title10-vol1-part20.pdf
[US standards,USNRC standards,Dose to public;page 357, item,20.1301]]
http://www.nucleartourist.com/events/NUREG-1465.pdf {Explosion emissions,USNRC Norms]
http://www.insipub.com/ajbas/2011/December-2011/1361-1364.pdf Pollutant Dispersion model]
http://www.radiation-scott.org/radsource/index.htm (Radiation doses and cancer)
http://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/educators/resources/evarm/grade11/affects.asp%20%20
(Basic radiation impacts)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/nuregs/staff/sr1437/supplement34/vegp-fseis-34.pdf
(a model EIA report submitted in USA for granting licence to Vogtle Nuclear Reactors in Georgia)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/cfr/part050/part050-apps.html
[ NRC ,USA Guidelines and standards on earthquake safety violated, see,para IV [a][1][i]
http://www.bredl.org/theleagueline/Summer2011.pdf
[ Pp-8,As per NRC standards, EarthQuake's PGA is 0.1g,so kudankulam is bound to fail]
http://www.energyjustice.net/nuclear [Routine pollution and impacts in USA]
http://www.reachingcriticalwill.org/resources/publications/costs-risks-myths/report.pdf [Myths of safety]
http://www.nirs.org/reactorwatch/licensing/licensingprocess.pdf [Reactor permit process in USA]
[US NRC publication on Accident scenario and impacts on health and other matters,2012]
http://www.nrc.gov/about-nrc/regulatory/research/soar/faqs.html [ public doubts on safety,USNRC]
http://pbadupws.nrc.gov/docs/ML1202/ML120250406.pdf [Accident scenario,NRC,USA]http://nidm.gov.in/PDF/guidelines/nuclear_radiological_emergencies.pdf
[ NDMA Guidelines on Nuclear Emergency preparedness plan] for Indian reactors ]
http://www.greenpeace.org/international/en/campaigns/nuclear/safety/ [Fukushima extends Zones]
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-13408055 ]Fukushima 30km.zone+$ 100 bn.costs Rs.5 lakh crores]
http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/article2615375.ece [Biggest lies of AEC officials]
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/health-12722435 [Fukushima ,health impacts]
http://science.howstuffworks.com/inside-nuclear-power-plant-pictures.htm
[Information on the Working of a Nuclear Plant with Figures]
http://www.iaea.org/Publications/Magazines/Bulletin/Bull254/25402043036.pdf
[IAEA study indicates that 60% Core Melt Downs occur due to Human failures]
http://www.rediff.com/news/column/india-corruption-nuclear-safety/20110318.htm [corrupt Deals?]
http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/fukushima_accident_inf129.html [Fu,kushima accident impacts]
http://www.nature.com/news/2011/110421/full/472400a.html [Reactors,people at Risk]
http://www.info.gov.za/view/DownloadFileAction?id=124577 [South Africa Reactors-Disasters]
http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/CFR-2011-title10-vol1/pdf/CFR-2011-title10-vol1-part20.pdf
[US standards,USNRC standards,Dose to public;page 357, item,20.1301]]
http://www.nucleartourist.com/events/NUREG-1465.pdf {Explosion emissions,USNRC Norms]
http://www.insipub.com/ajbas/2011/December-2011/1361-1364.pdf Pollutant Dispersion model]
http://www.radiation-scott.org/radsource/index.htm (Radiation doses and cancer)
http://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/educators/resources/evarm/grade11/affects.asp%20%20
(Basic radiation impacts)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/nuregs/staff/sr1437/supplement34/vegp-fseis-34.pdf
(a model EIA report submitted in USA for granting licence to Vogtle Nuclear Reactors in Georgia)
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/cfr/part050/part050-apps.html
[ NRC ,USA Guidelines and standards on earthquake safety violated, see,para IV [a][1][i]
http://www.bredl.org/theleagueline/Summer2011.pdf
[ Pp-8,As per NRC standards, EarthQuake's PGA is 0.1g,so kudankulam is bound to fail]
http://www.energyjustice.net/nuclear [Routine pollution and impacts in USA]
http://www.reachingcriticalwill.org/resources/publications/costs-risks-myths/report.pdf [Myths of safety]
http://www.nirs.org/reactorwatch/licensing/licensingprocess.pdf [Reactor permit process in USA]
http://www.isec.ac.in/WP%20232%20-%20P%20Srikant.pdf [ plant 50km from CEYLON]
http://www.barc.ernet.in/egreport.pdf {BARC report on kudankulam]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/main/MOEF_clearance_EIA_KKNPP.aspx [NPCIL Facts on Kudankulam]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/pdf/news_28sep2011_02.pdf [All EIA reports on kudankulam]
[Note: This article shows metaphorically how a a reactor failure causes impacts similar to Nuclear Bombs]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/pdf/A5.pdf
http://www.npcil.nic.in/main/MOEF_clearance_EIA_KKNPP.aspx [NPCIL Facts on Kudankulam]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/pdf/news_28sep2011_02.pdf [All EIA reports on kudankulam]
[Note: This article shows metaphorically how a a reactor failure causes impacts similar to Nuclear Bombs]
http://www.npcil.nic.in/pdf/A5.pdf
[Safety Evaluation of kudankulam Reactors in the lightr of Fukushima accident]
http://www.ieer.org/sdafiles/16-1.pdf [ Air and waterpollution from Tritium Releases,USA]
http://www.ieer.org/reports/npd7.html [Myths of Advanced passive safety Reactors]
http://www.world-nuclear.org/education/uran.htm [Uranium ore to Fuel and power production]
http://www.nuclearfaq.ca/Gentner-Osborne_PBNC_1998_paper.pdf ][Threshold Dose ..?]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Passive_nuclear_safety [ passive safety ststem Reactors]
http://www.dianuke.org/pmane-expert-team-first-report-15-11-2011/ [PMANE EXPERT'S REPORT]
http://www.ieer.org/sdafiles/16-1.pdf [ Air and waterpollution from Tritium Releases,USA]
http://www.ieer.org/reports/npd7.html [Myths of Advanced passive safety Reactors]
http://www.world-nuclear.org/education/uran.htm [Uranium ore to Fuel and power production]
http://www.nuclearfaq.ca/Gentner-Osborne_PBNC_1998_paper.pdf ][Threshold Dose ..?]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Passive_nuclear_safety [ passive safety ststem Reactors]
http://www.dianuke.org/pmane-expert-team-first-report-15-11-2011/ [PMANE EXPERT'S REPORT]
http://bhujangam.blogspot.in/2011/08/nuclear-power-is-inherently-hazardous.html
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/nuregs/staff/sr1437/supplement34/vegp-fseis-34.pdf
http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/nuregs/staff/sr1437/supplement34/vegp-fseis-34.pdf
(a model EIA report submitted in USA for granting licence to Vogtle Nuclear Reactors in Georgia)
AS AN IRRITATED SNAKE KILLS A MAN, NUCLEAR PLANTS SILENTLY KILL MANKIND AND NATURE FOR FINANCIAL GAINS BY CONTRACTORS,OFFICIALS& POLITICIANS ?
Nuclear Plants are just silent killers of man and Nature created by the GOD. In nature the Uranium ore contains 99.3% of Uranium-238 and the remaining 0.7% is Uranium-235. Uranium-238 and Uranium-235 in nature are least harmful. But business people and other vested interests dig the iron ore and convert the least harmful Uranium-235 into the fuel form of Uranium-235 by purifying it to make a fuel by enriching it to about 4% of Uranium-235 that is packed in pellets and inserted into the core of the nuclear reactor for producing both electricity and material for making the bombs. The reactor when the nuclear atom is given a blow by a neutron, enormous heat and other poisonous Radio-active atoms like Xenon, Baerium, Ceasium, Strontium, Plutonium and other dangerous radioactive substances are produced. These radioactive substances are discharged into the air and water by several ways and when they enter into the environment consisting of air, water and soil and foods like vegetables, fishes, prawns they ultimately get into human beings and produce cancers and birth defects in generations of people for many decades to come. These poisonous radioactive substances destroy natural and human life and culture and convert lands upto hundreds of kilometers into permanent nuclear burial grounds for ever.
How harmless Uranium ore materials in nature are converted into destructive and killer materials by man can be understood by the following simple example. For instance king cobras live in nature in anthills in forestsand lead their normal life peacefully by catching their prey for food during nights But greedy people go and poke their iron rods into their abodes and disturb the Cobras when they become angry and bite the trespassers to inflict death over them by their poisons. Similarly, the selfish people are mining the harmless Uranium and converting it into harmful Enriched Uranium and then using it to produce electricity by means of the Nuclear plants and in the process they are producing Radioactive pollutants that poison man and nature slowly due to routine releases of radioactivity into the environment .In course of time if an accident occurs in the Nuclear plant due to several reasons like in Fukushima or Chernobyl, the poisonous pollutants are thrown into the atmosphere and they kill thousands of people slowly and inflict cancer to millions of people living downstream upto hundreds of Kilometers as in case of Fukushima and Chernobyl accidents. The Nuclear plant operators are misleading the public by stating that Nuclear power is safe and cheap just like the medical representatives of various pharmaceutical companies praise before the doctors about the virtues of their medical tablets and tonics as part of their sale promotion activity the nuclear authorities are praising the nuclear plants as safe and cheap energy producers which is wrong. This misinformation is dangerous to public health and welfare because in European states almost all people agree that safety of Nuclear (power is a Myth as accepted by Angela Merkel, Chancellor of Germany. She had consulted the genuine experts on nuclear plants and realized that nuclear safety is a myth and ordered for gradual closure of all the nuclear plants in Germany. If Indian Prime Minister and Union Cabinet Minsters including the Chief Ministers of the state want to know the truth about the safety of the nuclear power plants they must go and visit advanced countries like Germany and Japan and discuss the issue with foreign experts so that they can refrain from promoting nuclear plants as is done by the peoples leader like Mamata Banerjee, Chief Minister of West Bengal. For more scientific details see the above web sites on this topic prepared by independent experts.
Environmental Impact Analysis report are fabricated by consultants according to the national Green Tribunal and also according to the Chief Justice of India, S.H.Kapadia who said “If you leave report preparation to the project proponent, I am sorry to say the person who pays will get the answers he asks for” and hence he called for a change in the system of preparation of EIA reports for the development projects. See website: http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/article2886141.ece
HOW INDIAN OFFICIALS ARE MISLEADING PEOPLE ON SAFETY OF NUCLEAR PLANTS
Prestigious Jonathan Mann Awardee for Health and Human rights Dr.Binayak Sen, a public health specialist and a noted human rights activist has rightly classified Kudankulam plant as an obvious huge human risk venture and the fact that the promoters of the plant are going ahead with it is a very shameful act. He pin pointed the risks posed by the plant to lakhs of people and the environment. He exhorted the people and the government to see if not for anything else what a heinous kind against mankind happened in Fukushima he questioned if we can dare to take risks by a repeat of Fukushima Nuclear explosion in India. Dr.Sen said that it is heartening to see the way the Kudankulam people had risen as a community and opposed the Nuclear plant to safeguard their human rights as guaranteed by the Indian constitution. In reply to the statement published in the Indian Express website on 27-1-2012 the Executive Director Dr.N.Nagaich of the Nuclear power Corporation of India gave rejoinder which is completely misleading and creates an impression that the Nuclear plant proposed at Kudankulam is indeed one of the safest Nuclear Plant built in the world till date. The nuclear power corporation authorities should have admitted the alarmist assertions about Kudankulam plant made by Dr.Binjayak Sen not merely in the context of the events at Fukushima in Japan but also a similar explosion in the Russian Nuclear Plant at Chernobyl and another Nuclear plant at Three Mile Island in the United States. Kudankulam nuclear plant is a very risky nuclear plant because the Russian reactors are inherently accident prone ones. These reactors can explode due to minor and medium failures designated as excursions. Even if there is a slight leakage or breakage in the pipes or the cooling water pumps and if they are not attended to within 45 seconds a minor accident is bound to result in catastrophic failure which causes a core melt down whose damaging impacts extend upto hundreds of kilometers alround depending upon the fluctuating speeds and directions of the wind and it requires emergency evacuation upto 20km in the first stage within a few hours and further evacuation upto 80km within one or 2 days failing which besides the public health hazards the economic loss grows upto 4 lakh crores of rupees on the basis of costs of damage due to Fukushima reactor explosion. The Kudankulam nuclear site has not at all been studied from the public safety angle and reactor safety as per the conditions stipulated under 10 guidelines formulated by the International Atomic Energy Agency. The tsunami in 2004 recorded 10m high sea water in a nearby place at Nagarcoil and hence this Kudankulam plant must be considered under designed from this angle. Kudankulam seismic potential has not been studied by using the helicopters fitted with magneto meters to map the geological anomalies to identify the hidden faults under activation by conducting a grid based air-borne survey on the lines of similar studies being conducted in Oregaon Portland Vancouver in Western USA. Since the area is located on land mass is subjected to getting pushed under the Tibetan plate the cymatogenic arches and deeps may cause serious tremors that may damage the nuclear plant. The contention of NPCIL that their evaluation of seismic potential based on the selection committee report that imposed limitations by the criteria imposed by the Atomic Energy Regulatory Board which itself may not be a competent agency to ensure seismic safety of the site.
While the NPCIL claims that the Reactors are indeed among safest in the world and that safety is the top most priority for the plant promoters they should have the courage to publish the environmental impact assessment reports for the proposed reactors by demonstrating to the public. The details of the reports on reactor explosion analysis for the emission factors, their dispersal rates and their deposition on the ground upto 20km for the first evacuation zone and upto 80km for emergency planning alround the plant as adopted for the nuclear plants in United States and upto 100km as followed in European countries like Finland. If these reports are prepared they must be placed before the concerned public and widely discussed for grasping the public opinion for enlisting their cooperation and consent along with their readiness to evacuate their residences, offices and cattle wealth for several years in case of an accident and return back to their homes after decontamination for periods of 5 to 20 years. If the Nuclear plant authorities have ethical and moral standards and have public interest at heart they should prevail over the Government of India to desist from imposing mass scale penalties in the form of taxation for using that amount to meet the costs of damage due to a Nuclear Power Plant accident resulting in a huge economic loss of about 5 lakh crores of rupees that makes the country become economically bankrupt, ecologically risky and environmentally disastrous. By imparting cancer and other forms of illness for millions of people around the Kudankulam nuclear plant. The nuclear plant may fail for several reasons including terrorist attacks, internal sabotage, electrical or mechanical failures or human failures which if not rectified in the case of a loss of coolant accident caused by rupturing of cooling water pipelines and pumps within 45 seconds such accidents may lead to core melt down and a nuclear plant explosion like the ones that occurred in Chernobyl in 1986 and Fukushima in 2011.
PASSIVE SAFETY REACTORS CANNOT BE SAFE IF SECURITY IS VIOLATED BY BOMBING
The overlapping safety systems that include both active and passive features cannot ensure safety of the advanced design reactors that use passive mechanisms for natural air circulation based on conviction. During the trial runs in the United States it was established that passive safety reactors will also fail quite often. These systems are bound to fail if they are subjected to aerial bombing by enemy countries just as the British bombs were thrown by the aeroplanes over the dams in Germany
http://www.dianuke.org/koodankulam-sasikumar-3/[Failure modes of passive safety systems in Reactors]
Since Kudankulam is located close to Srilanka there is every possibility for sabotage, terrorist attacks and bombing which result in nuclear plant accidents at Kudankulam. Thus the selection of sites itself in close proximity to terrorist activities and vulnerable to bombing by enemy countries is itself a grave crime perpetrated by the Union Government under the guise of nuclear power generation which itself contributes only about 3% of the total energy demands of country at a very exorbitant cost and by taking very risky and hazardous reactors while the same amount of energy can be produced by cheaper and very safe alternate technologies like thermal power, hydro-power and power based on use of oil and natural gas which are available plenty in the country. Hence the promotion of highly costly and most risky nuclear power plants without the consent of the people in a social welfare state amounts to an action much worse than the action taken by the dictator like Hitler to wipe out Jews in the concentration camp during the second world war. Thus the promotion of nuclear power plants amounts to an undeclared war against lakhs of innocent people in the Southern districts of Tamilnadu and Kerala.
But Indian state and Central Governments are just ignoring public safetry by violating International standards and thereby making an undeclared Nuclear war with the millions of poor people of the southern districts of Tamilnadu and Kerala where people have forgotten Mahatmaji's Slogan "Eternal Vigilance is the Price you have to Pay for Sustaining the Social Welfare State and Mrs.Indira Gandhi also amended Art.51A[g] of the Indian Constitution by making it the responsiblity of Every indian to protect the Water,the Air,the forests and wild life and to develop compassion for all living creatures"
But where can we find such patriotic and honest indians who can fight for saving the democratic right to life and the right to livelihood?Indian educated people have lost the capacity to think rationally and act to save the Nation including its people and Natural assests as otherwise they should go to Germany and Japan to learn from their Prime ministers how nuclear safety is a Myth not only to knosw the truth but also to save the nation
PASSIVE SAFETY REACTORS CANNOT BE SAFE IF SECURITY IS VIOLATED BY BOMBING
The overlapping safety systems that include both active and passive features cannot ensure safety of the advanced design reactors that use passive mechanisms for natural air circulation based on conviction. During the trial runs in the United States it was established that passive safety reactors will also fail quite often. These systems are bound to fail if they are subjected to aerial bombing by enemy countries just as the British bombs were thrown by the aeroplanes over the dams in Germany
http://www.dianuke.org/koodankulam-sasikumar-3/[Failure modes of passive safety systems in Reactors]
Since Kudankulam is located close to Srilanka there is every possibility for sabotage, terrorist attacks and bombing which result in nuclear plant accidents at Kudankulam. Thus the selection of sites itself in close proximity to terrorist activities and vulnerable to bombing by enemy countries is itself a grave crime perpetrated by the Union Government under the guise of nuclear power generation which itself contributes only about 3% of the total energy demands of country at a very exorbitant cost and by taking very risky and hazardous reactors while the same amount of energy can be produced by cheaper and very safe alternate technologies like thermal power, hydro-power and power based on use of oil and natural gas which are available plenty in the country. Hence the promotion of highly costly and most risky nuclear power plants without the consent of the people in a social welfare state amounts to an action much worse than the action taken by the dictator like Hitler to wipe out Jews in the concentration camp during the second world war. Thus the promotion of nuclear power plants amounts to an undeclared war against lakhs of innocent people in the Southern districts of Tamilnadu and Kerala.
FUKUSHIMA ACCIDENT FORCED JAPAN TO EVACUATE VICTIMS UPTO 40Km.from REACTORS as pper web site:
http://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/nuke/R41694.pdfBut Indian state and Central Governments are just ignoring public safetry by violating International standards and thereby making an undeclared Nuclear war with the millions of poor people of the southern districts of Tamilnadu and Kerala where people have forgotten Mahatmaji's Slogan "Eternal Vigilance is the Price you have to Pay for Sustaining the Social Welfare State and Mrs.Indira Gandhi also amended Art.51A[g] of the Indian Constitution by making it the responsiblity of Every indian to protect the Water,the Air,the forests and wild life and to develop compassion for all living creatures"
But where can we find such patriotic and honest indians who can fight for saving the democratic right to life and the right to livelihood?Indian educated people have lost the capacity to think rationally and act to save the Nation including its people and Natural assests as otherwise they should go to Germany and Japan to learn from their Prime ministers how nuclear safety is a Myth not only to knosw the truth but also to save the nation
Environmental Impact Analysis report are fabricated by consultants according to the national Green Tribunal and also according to the Chief Justice of India, S.H.Kapadia who said “If you leave report preparation to the project proponent, I am sorry to say the person who pays will get the answers he asks for” and hence he called for a change in the system of preparation of EIA reports for the development projects. See website: http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/article2886141.ece
NUCLEAR SAFETY IS NOT ONLY REACTOR SAFETY BUT ALSO PUBLIC SAFETY AS ENVISAGED BY THE GUIDELINES OF THE IAEA and NPCIL IS IGNORANT OF SAFETY:
Nuclear Reactor safety is not only based primarily on proper design and construction of the nuclear plant including the engineered multi-layered safety features under the policy of defence indepth but also secondarily by demonstration of the proof in termsof the skills and abilities of the nuclear plant authorities and the local state government and panchayat institutions to not only chalk out but also implement the public health protection measures has contemplated by the emergency preparedness plans to be activated during the course of the travel of the radioactive plume caused by the accidental nuclear plant explosion..
EVEN STRESS TESTS FAILED FOR JAPANESE REACTORS ON 4-4-2012
a]
Oettinger said the STRESS TESTS were strict and objective and sought to establish whether nuclear plants could withstand natural disasters, aircraft crashes, management failures and what systems were in place to deal with power disruptions
http://www.reuters.com/article/2012/03/06/nuclear-stress-idUSL5E8E61ZE20120306
INDIA DOES NOT NEED NUCLEAR PLANTS AS THERE ARE SAFER ALTERNATE ENERGY SOURCES LIKE NATURAL GAS, CRUDE OIL AND COAL WHICH ARE ALSO CHEAPER AS CAN BE SEEN BY THE FOLLOWING PRESENTATION
STOCKS OF ENERGY SOURCES AND RESERVES IN INDIA
The Indian Ocean’s seven large (M>7.0) “intraplate” earthquakes include the largest oceanic “intraplate” earthquake known, the 1928,M7.7 Ninetyeast Ridge event. The level of “intraplate” seismicity is unequaled; the only other magnitude 7 oceanic intraplate earthquakes occur at passive continental margins (Stein et.al., 1979) or sites of active volcanism like Hawaii.
http://library.lanl.gov/tsunami/ts241.pdf
(Volume 24, Number1, 2006)
(Volume 24, Number1, 2006)
(Science of Tsunami Hazards, Vol 17, NO. 3 (1999) page 167 )
"Even though earthquakes occur frequently in India and in the surrounding waters, tsunami events are rare. No matter how rare they may be, they cannot be totally ignoredin terms of public safety as well as safety of the coastal infrastructure. " said the authors of the paper by Bapat and Tad Murthy, experts in Tsunami hazards.
The devastating tsunami that occurred in December, 2004 near Indonesia has lifted the sea water to such a great height on the Eastern side of the fault that forced a very great height of water wave to jump from East to West creating a very massive and powerful tsunami which was forced to travel westward and cause devastation by creating a very high wave of flood water that killed thousands of people on the East and West coast of India and Ceylon. Since Kudankulam area was virtually protected by the vast land masses on the North, East and Southern sides covering Pamban bridge, Jafna and Ceylon Islands the impact of the Tsunami water wave was drastically reduced and hence the Tsunami wave heights recorded at Kudankulam were very low although Kanyakumari faced wave heights upto 9 to 10m. But the enclosed sketches covering the seismicityof 90degrees East ridge and the Chagos ridge which previoously experienced earthquakes of over 7 magnitude can generate high tsunami waves on the southern side of Ceylon which may directly hit Kudankulam and when the natural obstacles in the sea from Pamban bridge to Jafna can riverbret the sea waves which may be magnified by the configuration of land over West Ceylon and hence the wave heights at Kanyakumari will be highly magnified and consequently Kudankulam may experienced greater magnitudes of flood heights due to the Tsunami generated by the interpenetratiang tectonic plates on the South of Ceylon. Hence the Kudankulam nuclear plant may be treated as an underdesigned plant in respect of both earthquake impacts and tsunami impacts arising from the sources in the Indian Ocean on the South of Indian Peninsula and Ceylon Islands. This is a very crucial aspect that may cause a nuclear reactor accident at Kudankulam.
IN USA GEORGIA STATE FINDS NUCLEAR POWER COSTLIER THAN NATURAL GAS etc.
80KM EPZ FOR US REACTORS
EMERGENCY PLANNING ZONES FOR NUCLEAR ACCIDENTS, IAEA


http://fukushima.greenaction-japan.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/04/PSR_Statement_on_Fukushima_Children.pdf
http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=11340&page=1 (See this book for scientific details)
(There is no minimum safe radiation level for cancer as natural radiation also causes more cancers)
JAPAN PRIME MINISTER TELLS THE WORLD ABOUT MYTHS OF NUCLEAR SAFETY:
The huge storm that battered the Kanto and Hokuriku parts of Japan on Tuesday night temporarily reduced electricity supplies to the Onagawa nuclear power plant in Miyagi Prefecture, halting the cooling system for a fuel pool, operator Tohoku Electric Power Co said Wednesday.
Plant workers manually restarted the cooling system after about 20 minutes, it said. “There was no problem in the operation,” a company spokesman said..All reactors at the plant are currently idle..
http://www.japantoday.com/category/national/view/storn-briefly-halts-cooling-system-for-fuel-pool-at-onagawa-nuclear-power-plant?utm_campaign=jt_newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_source=jt_newsletter_2012-04-04_PM
IN USA GEORGIA STATE FINDS NUCLEAR POWER COSTLIER THAN NATURAL GAS etc.
NUCLEAR POWER IS NOT AT ALL NECESSARY DUE TO SAFER AND CHEAPER ALTERNATIVE SOURCES OF ENERGY
Indian Energy Scenario
Coal dominates the energy mix in India, contributing to 55% of the total primary energy production. Over the years, there has been a marked increase in the share of natural gas in primary energy production from 10% in 1994 to 13% in 1999. There has been a decline in the share of oil in primary energy production from 20% to 17% during the same period.
Energy Supply
Coal Supply
India has huge coal reserves, at least 84,396 million tonnes of proven recoverable reserves (at the end of 2003). This amounts to almost 8.6% of the world reserves and it may last for about 230 years at the current Reserve to Production (R/P) ratio. In contrast, the world’s proven coal reserves are expected to last only for 192 years at the current R/P ratio.
Reserves/Production (R/P) ratio- If the reserves remaining at the end of the year are divided by the production in that year, the result is the length of time that the remaining reserves would last if production were to continue at that level. India is the fourth largest producer of coal and lignite in the world. Coal production is concentrated in these states (Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Orissa, Jharkhand, West Bengal).
Oil Supply
Oil accounts for about 36 % of India's total energy consumption. India today is one of the top ten oil-guzzling nations in the world and will soon overtake Korea as the third largest consumer of oil in Asia after China and Japan. The country’s annual crude oil production is peaked at about 32 million tonne as against the current peak demand of about 110 million tonne. In the current scenario, India’s oil consumption by end of 2007 is expected to reach 136 million tonne(MT), of which domestic production will be only 34 MT. India will have to pay an oil bill of roughly $50 billion, assuming a weighted average price of $50 per barrel of crude. In 2003-04, against total export of $64 billion, oil imports accounted for $21 billion. India imports 70% of its crude needs mainly from gulf nations. The majority of India's roughly 5.4 billion barrels in oil reserves are located in the Bombay High, upper Assam, Cambay, Krishna-Godavari. In terms of sector wise petroleum product consumption, transport accounts for 42% followed by domestic and industry with 24% and 24% respectively. India spent more than Rs.1,10,000 crore on oil imports at the end of 2004.
The ever rising import bill
|
| ||
Year
|
Quantity (MMT)
|
Value (Rs Crore)
| |
1996-97
|
33.90
|
18,337
| |
1997-98
|
34.49
|
15,872
| |
1998-99
|
39.81
|
19,907
| |
1999-00
|
57.80
|
40,028
| |
2000-01
|
74.10
|
65,932
| |
2001-02
|
84.90
|
8,116
| |
2002-03
|
90
|
85,042
| |
2003-04
|
95
|
93,159
| |
*2004-05
|
100
|
1,30,000
| |
* Estimated
Source: Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas
| |||
Natural Gas Supply
Natural gas accounts for about 8.9 per cent of energy consumption in the country. The current demand for natural gas is about 96 million cubic metres per day (mcmd) as against availability of 67 mcmd. By 2007, the demand is expected to be around 200 mcmd. Natural gas reserves are estimated at 660 billion cubic meters.
Electrical Energy Supply
The all India installed capacity of electric power generating stations under utilities was 1,12,581 MW as on 31st May 2004, consisting of 28,860 MW- hydro, 77,931 MW - thermal and 2,720 MW- nuclear and 1,869 MW- wind (Ministry of Power).
The gross generation of power in the year 2002-2003 stood at 531 billion units (kWh).
Nuclear Power Supply
Nuclear Power contributes to about 2.4 per cent of electricity generated in India. India has ten nuclear power reactors at five nuclear power stations producing electricity. More nuclear reactors have also been approved for construction.
Hydro Power Supply
India is endowed with a vast and viable hydro potential for power generation of which only 15% has been harnessed so far. The share of hydropower in the country’s total generated units has steadily decreased and it presently stands at 25% as on 31st May 2004. It is assessed that exploitable potential at 60% load factor is 84,000 MW.
Final Energy Consumption
Final energy consumption is the actual energy demand at the user end. This is the difference between primary energy consumption and the losses that takes place in transport, transmission & distribution and refinement. The actual final energy consumption (past and projected) is given in Table 1.2.
Table 1.2 DEMAND FOR COMMERCIAL ENERGY FOR FINAL CONSUMPTION (BAU SCENARIO)
| |||||
Source
|
Units
|
1994-95
|
2001-02
|
2006-07
|
2011-12
|
Electricity
|
Billion Units
|
289.36
|
480.08
|
712.67
|
1067.88
|
Coal
|
Million Tonnes
|
76.67
|
109.01
|
134.99
|
173.47
|
Lignite
|
Million Tonnes
|
4.85
|
11.69
|
16.02
|
19.70
|
Natural Gas
|
Million Cubic Meters
|
9880
|
15730
|
18291
|
20853
|
Oil Products
|
Million Tonnes
|
63.55
|
99.89
|
139.95
|
196.47
|
Source: Planning Commission BAU:_Business As Usual
| |||||
Sector wise Energy Consumption in India
The major commercial energy consuming sectors in the country are classified as shown in the Figure 1.5. As seen from the figure, industry remains the biggest consumer of commercial energy and its share in the overall consumption is 49%. (Reference year: 1999/2000)
http://www.em-ea.org/Guide%20Books/Book-1/1.1%20Energy%20Scenario.pdf
IS RADIATION EXPOSURE BETWEEN 50 Rems[Rads] and 100 Rads[REMS]per year improve Health? Does Low Level Radiation promote Homeosis by acgtivating immunity and cell Repair systems ?
http://www.hiroshimasyndrome.com/radiation-the-no-safe-level-myth.htm
IS RADIATION EXPOSURE BETWEEN 50 Rems[Rads] and 100 Rads[REMS]per year improve Health? Does Low Level Radiation promote Homeosis by acgtivating immunity and cell Repair systems ?
http://www.hiroshimasyndrome.com/radiation-the-no-safe-level-myth.htm
Effective Work culture as a weapon to fight Nuclear Reactor Accidents.
AERB EMERGENCY PLANNING ZONES FOR NUCLEAR ACCIDENTS
Depending on the nature and severity of accident, the effect of the emergency may
be restricted to either a small area of the plant or a few individuals or it may pause
danger to the plant itself. In more severe cases, release of from the plant may
contaminate the site within the site boundary or can propagate outside the site
boundary. Taking these into consideration, emergency situations are classified as
1) plant emergency alert,
be restricted to either a small area of the plant or a few individuals or it may pause
danger to the plant itself. In more severe cases, release of from the plant may
contaminate the site within the site boundary or can propagate outside the site
boundary. Taking these into consideration, emergency situations are classified as
1) plant emergency alert,
2) plant emergency,
3) site emergency, and
4) off-site emergency.
While the operating organization of the plant are responsible for handling the first three categories of emergencies,
While the operating organization of the plant are responsible for handling the first three categories of emergencies,
off-site emergencies are handled by the State authorities with the technical input and guidance from operating organization of the plant and regulatory authority.
During siting stage, the relevant site features that have a bearing on the various
protective measures that may need to be initiated following an off-site emergency
condition are assessed. The area within 16km radius of plant is designated as
emergency planning zone (EPZ), Figure-2. The off-site emergency planning is
prepared for this zone.
During siting stage, the relevant site features that have a bearing on the various
protective measures that may need to be initiated following an off-site emergency
condition are assessed. The area within 16km radius of plant is designated as
emergency planning zone (EPZ), Figure-2. The off-site emergency planning is
prepared for this zone.
The relevant information required for estimation of dose to
public such as population data, land and water use, dietary habits, etc are collected,
upto a radial distance of 30km. Full details of population distribution sector wise (16
sectors of 22.5 degrees in EPZ) is also obtained. It is ensured that population data
takes into account all people employed at site including construction workers, if any.
As cattle milk forms an intermediate pathway in the ingestion route for children,
data on cattle population in rural areas is another input in the preparation of
emergency plans for nuclear power plants.
While preparing the off-site emergency management plan, inputs/information of the
State government machinery, evacuation routes including road and railway network
in EPZ, communication facilities, buildings for sheltering both inside and outside
EPZ, medical facilities, transport facilities, etc are assimilated and emergency
management plans are prepared.
public such as population data, land and water use, dietary habits, etc are collected,
upto a radial distance of 30km. Full details of population distribution sector wise (16
sectors of 22.5 degrees in EPZ) is also obtained. It is ensured that population data
takes into account all people employed at site including construction workers, if any.
As cattle milk forms an intermediate pathway in the ingestion route for children,
data on cattle population in rural areas is another input in the preparation of
emergency plans for nuclear power plants.
While preparing the off-site emergency management plan, inputs/information of the
State government machinery, evacuation routes including road and railway network
in EPZ, communication facilities, buildings for sheltering both inside and outside
EPZ, medical facilities, transport facilities, etc are assimilated and emergency
management plans are prepared.
80KM EPZ FOR US REACTORS
EMERGENCY PLANNING ZONES FOR NUCLEAR ACCIDENTS, IAEA
The
document [4] requires that for facilities in threat category I or
II,arrangements shall be made for effectively making and implementing decisions
on urgent protective actions to be taken off the site within:
(a) a PAZ, for
facilities in threat category I, within which arrangements shall be made with
the goal of taking precautionary urgent protective action, before a release of
radioactive material occurs or shortly after a release of radioactive material begins,
on the basis of conditions at the facility (such as the emergency
classification) in order to reduce substantially the risk of severe
deterministic effects.
(b) an UPZ, for
facilities in threat category I or II, within which arrangements shall be made
for urgent protective action to be taken promptly, in accordance either with
international or national standards, in order to avert dose off the site.
The PAZ and UPZ
should be roughly circular areas around the facility, their boundaries should
be defined, where appropriate, by local landmarks (e.g. roads or rivers) to
allow easy identification during a response as illustrated in Fig. 4.1. It is
important to note that the zones should not stop at national borders. The size of
the PAZ and the UPZ should be consistent with the guidance provided in Appendix
II of [5].
(c) In addition
to PAZ and UPZ, there is also a Food Restriction Planning Zone(FRPZ), which is more
often called Longer-term Protective action Zone (LPZ).
This is an area
around the facility where preparations for effective implementation of
protective actions to reduce the long term dose, i.e. the risk of stochastic
health effects5
from
deposition and ingestion of locally grown food, should be developed in advance.
The longer term protective action zone will of course include the PAZ and the
UPZ and extend to a further radius. On the bases of severe accident studies,
the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission (USNRC) for instance has
adopted this zone of 80 km (50 miles), however, it might be much larger, up to
a couple of hundreds of kilometres.
On-Site: Internal zone,
under control of NPP operator
PAZ: Precautionary
Action Zone UPZ: Urgent
Protective action planning Zone
LPZ:
Long-term Protective Zone (Food Restriction Planning Zone-FRPZ)
[12]. The
calculations assumed average meteorological conditions, no rain, ground level
release; 48 hours of exposure to ground shine, and calculates the centralized
dose to a person outside for 48 hours. The suggested sizes for the PAZ were
based on expert judgment considering the following:
The AERB Code of Practice on Safety in
Nuclear Power Plant Siting states: An exclusion area of appropriate size (at
least 1.5 km radius from the reactor centre) shall be established around the
reactor and entry to this is to be restricted to authorized personnel only. Thus
the population falling within the exclusion zone, if any, is only resettled. The sterilized zone is the annulus
between the exclusion zone and an area up to 5 km from the plant. The AERB code
states in this regard:
“A sterilised area up to 5 km around the plant shall be established
by administrative measures where the growth of population will be restricted
for effective implementation of emergency measures. Natural growth, however, is
allowed in this zone”. Thus,
there is no displacement involved in the sterilized zone.
In fact, there are no restrictions on
natural growth of population in the sterilized zone. The administrative measures
are put in place to ensure that there is no large increase in the population
due to say setting up of an industry involving large labour force, etc.
( TASK FORCE ON SAFETY EVALUATION OF THE SYSTEMS OF KKNPP POST FUKUSHIMA EVENT)
http://fukushima.greenaction-japan.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/04/PSR_Statement_on_Fukushima_Children.pdf
http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=11340&page=1 (See this book for scientific details)
(There is no minimum safe radiation level for cancer as natural radiation also causes more cancers)
TAMILNADU GOVERNMENT EXPERT COMMITTEE ON KUDANKULAM
Tamilnadu Chief Minister CM Jayalalithaa today named 4 member committee to analyse the safety and assess people's fear.
1) M.R. Srinivasan, former Chairman, Atomic Energy Commission and member of the experts committee,
2) S. Iniyan, Director of Centre for Energy Studies, Anna University,
Professor, Director center for Energy Studies,
3) D. Arivuoli, Professor, Department of Physics, Anna University
Professor, Department of Physics, Anna University - Chennai, INDIA and Editorial Board Member, International Journal of Bio Sciences and Technology . Dr. D. Arivuoli, Professor of Physics, Anna University did his MSc Materials science and PhD (crystal growth) at Anna University Chennai, INDIA.
4) L.N. Vijayaraghavan , former IAS office are the other members on the committee.
B.Com(Hons),M.Com, I.A.S(72:TN) Principal Commissioner& Commissioner of Civil Supplies, Plot 986, TVS Colony, Anna Nagar Western Extension, Chennai-600101, Tamil Nadu 26547170 ® ccs@tn.gov.in
JAPAN PRIME MINISTER TELLS THE WORLD ABOUT MYTHS OF NUCLEAR SAFETY:
Noda says world must not fall for 'myth of safety' over nuclear plants
The tsunami-triggered meltdown at a Japanese nuclear power plant last year offered important lessons in protecting such facilities from terrorism, Prime Minister Yoshihiko Noda said Tuesday.
Noda told a nuclear security summit in South Korea that people in charge of securing nuclear energy facilities around the world must not be lulled into a “myth of safety,” whether in regards to a natural disaster or terrorist attack.
Noda said the disaster at the plant at Fukushima had shown the difficulties in preparing for the worst-case scenario, when officials could not comprehend the scale of the threat to the nuclear power plant.
In the case of Fukushima, officials had only prepared for a tsunami just over five meters, but the the waves that swamped the coastal plant were three times higher, according to Noda.
“The workings of nature are beyond comprehension, but there is also no limit to human imagination,” Noda told the leaders or top officials from 53 nations attending the summit, including U.S. President Barack Obama.
“We should keep in mind that the man-caused act of sabotage will test our imaginations far more than any natural disaster.”
Noda said the most important lesson to be learned from the Fukushima meltdown was that there was no end in the efforts to ensure safety. “Every person who works toward nuclear security should take this to heart,” he said.
Noda said there was a need to establish procedures to quickly respond to emergencies and have off-site emergency power backup systems situated some distance from the power plants.
He said one of the problems in the immediate aftermath was a lack of coordination between civil and defense authorities and a difficulty in obtaining accurate information from the Fukushima plant. At times, it was difficult to know who was in charge, he said.
TEPCO executives should face poverty over Fukushima, lawyer says
National Mar. 27, 2012 - 11:20AM JST
TOKYO —
A lawyer representing shareholders suing Fukushima nuclear plant operator TEPCO for 5.5 trillion yen said Monday the company’s executives should be prepared for misery and poverty to make amends.
Hiroyuki Kawai, who is leading 42 shareholders in their bid for compensation from Tokyo Electric Power Company for negligence over the tsunami-sparked disaster at the plant, said senior managers must be made to pay.
“Warnings have to be issued that, if you make wrong decisions or do wrong, you must compensate with your own money,” Kawai told a press conference.
“You may have to sell your house. You may have to spend your retirement years in misery. In Japan, nothing can be resolved and no progress can be made without assigning personal responsibility.”
The lawsuit, which is demanding a record 5.5 trillion yen, claims that 27 current and former executives of TEPCO ignored warnings by researchers about the possible damage to the Fukushima Daiichi plant that a huge earthquake and tsunami could cause.
The Fukushima crisis might have been prevented, had TEPCO taken the research seriously and carried out simple preventative measures, such as placing an emergency power source on higher ground, Kawai said.
Reactors at the plant were sent into meltdown when huge waves swamped their cooling systems following the March quake.
Radiation leaked over a large area, forcing tens of thousands of people from their homes and rendering vast areas unfarmable.
No one from TEPCO has been arrested and there is no active criminal investigation into the case, despite a number of inquiries that found serious shortcomings in the company’s emergency safety procedures.
TEPCO declined to immediately comment on the ongoing civil case.
EVEN STRESS TESTS ON JAPAN REACTORS FAILED TO ENSURE SAFETY IN APRIL<2012
EVEN STRESS TESTS ON JAPAN REACTORS FAILED TO ENSURE SAFETY IN APRIL<2012
Oettinger said the STRESS TESTS were strict and objective and sought to establish whether nuclear plants could withstand natural disasters, aircraft crashes, management failures and what systems were in place to deal with power disruptions
http://www.reuters.com/article/2012/03/06/nuclear-stress-idUSL5E8E61ZE20120306http://www.japantoday.com/category/national/view/storn-briefly-halts-cooling-system-for-fuel-pool-at-onagawa-nuclear-power-plant?utm_campaign=jt_newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_source=jt_newsletter_2012-04-04_PMPlant workers manually restarted the cooling system after about 20 minutes, it said. “There was no problem in the operation,” a company spokesman said..All reactors at the plant are currently idle..
http://www.japantoday.com/category/national/view/storn-briefly-halts-cooling-system-for-fuel-pool-at-onagawa-nuclear-power-plant?utm_campaign=jt_newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_source=jt_newsletter_2012-04-04_PM
RADIATION DEFINITIONS
Alpha Decay: The emission of a nucleus of a helium atom from the nucleus of an element, generally of a heavy element, in the process of its radioactive decay.
Alpha Irradiation: Radiation with alpha particles.
Alpha Particle: A positively charged particle ejected spontaneously from the nuclei of some radioactive elements. It is identical to a helium nucleus that has a mass number of 4 and an electric charge of +2. It has low penetrating power and a short range (a few centimeters in air). The most energetic alpha particle will generally fail to penetrate the dead layers of cells covering the skin and can be easily stopped by a sheet of paper. Alpha particles represent much more of a health risk when emitted by radionuclides deposited inside the body.
Beta Decay: The emission of electrons or positrons (particles identical to electrons, but with a positive electrical charge) from the nucleus of an element in the process of radioactive decay of the element.
Beta Particle:A charged particle emitted from a nucleus during radioactive decay, with a mass equal to 1/1837 that of a proton. A negatively charged beta particle is identical to an electron. A positively charged beta particle is called a positron. Exposure to large amounts of beta radiation from external sources may cause skin burns (erythema). Beta emitters can also be harmful if they enter the body. Thin sheets of metal or plastic may stop beta particles.
Beta Radiation:Radiation consisting of beta particles.
Electromagnetic Radiation:A traveling wave motion resulting from changing electric or magnetic fields. Familiar types of electromagnetic radiation range from x rays (and gamma rays) of short wavelength, through the ultraviolet, visible, and infrared regions, to radar and radio waves of relatively long wavelength. Only the higher-energy (higher frequency/shorter wavelength) forms of electromagnetic radiation are ionizing. Radiation in the lower-energy ranges, such as visible, infrared, radar, and radio waves, are nonionizing.
Electron:An elementary particle with a negative charge and a mass 1/1837 that of the proton. Electrons surround the positively charged nucleus of the atom.
Gamma Radiation:High-energy, short wavelength, electromagnetic radiation emitted from the nucleus of an atom. Gamma radiation frequently accompanies the emission of alpha and beta particles and always accompanies fission.
Gamma Rays:Very penetrating and are best stopped or shielded by dense materials, such as lead or uranium. Gamma rays are similar to x-rays.
Ion:(1) An atom that has too many or too few electrons, causing it to have an electrical charge, and therefore, to be chemically active. (2) An electron that is not associated (in orbit) with a nucleus.
Ionization:The process of adding to or removing one or more electrons from atoms or molecules, thereby creating ions and free radicals. High temperatures, metabolic processes, electrical discharges, and radiation can cause ionization.
Ionize:To split off one or more electrons from an atom, thus leaving it with a positive electric charge. The electrons usually attach to other atoms or molecules, giving them a negative charge.
Ionizing Radiation:Any radiation capable of displacing electrons from atoms or molecules, thereby producing ions. Some examples are alpha, beta, gamma, x-rays, neutrons, and ultraviolet light.
Unit of Activity:
Units of Activity (Ci):
|
Units of Activity (Bq):
|
1 Centi Ci = 0.01 Ci
|
1 Kilo Bq (kBq) = 1,000 Bq
|
Milli 0.0001 Ci
|
Mega (MBq) 1,000,000 Bq
|
Micro 0.00001 Ci
|
Giga (GBq) 1,000,000,000 Bq
|
Nano 0.00000001 Ci
|
Tera (TBq) 1,000,000,000,000 Bq
|
Pico 0.000000000001 Ci
|
Peta (PBq) 1,000,000,000,000,000 Bq
|
Weightage Factors for Damaging impacts of different Radio-active substances on Human Body.
| Radiation | Energy | wR (also RBE or Q) |
|---|---|---|
| x-rays, gamma rays, electrons, positrons, muons | 1 | |
| neutrons | < 10 keV | 5 |
| 10 keV - 100 keV | 10 | |
| 100 keV - 2 MeV | 20 | |
| 2 MeV - 20 MeV | 10 | |
| > 20 MeV | 5 | |
| protons | > 2 MeV | 2 |
| alpha particles, nuclear fission products, heavy nuclei | 20 |
Even lowest Radiation dose causes serious health hazards in man and other forms of life:
It is estimated by scientific experts that in normal human cells about 1% of single-strand lesions are converted to about 50 EDSBs (Endogenous Double Strand Breaks in DNA) per cell per cell cycle. This number is similar to that for EDSBs produced by 1.5–2.0 Gy of sparsely ionizing radiation. Although EDSBs are usually repaired with high fidelity (reliability), the errors in their repair mechanisms contribute significantly to the rate of cancer in humans. The doubling dose for induced DSBs (Double Strand Breaks) is similar to doubling doses for mutation and for the induction of carcinomas by ionizing radiation. Hence Experts conclude that rates of production of EDSBs and of ensuing spontaneous mitotic recombination events can account for a substantial fraction of the earliest oncogenic events in human carcinomas. Thus nuclear reactor safety becomes a big Myth.
WIND ROSES FROM VARIOUS METEOROLOGICAL STATIONS AROUND THE NUCLEAR PLANT FROM INDIA AND ALSO SRILANKA TO SHOW FLUCTUATING WINDS
http://www.windfinder.com/windstats/windstatistic_mannar.htm
http://doh.wa.gov/ehp/hanford/publications/history/release.html#Soil
Three Mile Island Nuclear Plant explosion in USA, and its impacts ,28 March 1979
A major accident at the Three Mile Island nuclear plant near Middletown, Pennsylvania. At 4:00 a.m. a series of human and mechanical failures nearly triggered a nuclear disaster. By 8:00 a.m., after cooling water was lost and temperatures soared above 5,000 degrees, the top portion of the reactor's 150-ton core melted. Contaminated coolant water escaped into a nearby building, releasing radioactive gasses, leading as many as 200,000 people to flee the region. Despite claims by the nuclear industry that "no one died at Three Mile Island," a study by Dr. Ernest J. Sternglass, professor of radiation physics at the University of Pittsburgh, showed that the accident led to a minimum of 430 infant deaths. |
RADIOACTIVE AIR POLLUTION
Estimates of Radiation Released into the Air by Hanford, 1944-1972
Radionuclide
|
Amount Released (curies)
|
Half-Life
|
Iodine-131
|
740,000
|
8 days
|
Tritium (H-3)
|
200,000
|
12 years
|
Cobalt-60
|
1
|
5 years
|
Krypton-85
|
19,000,000
|
11 years
|
Strontium-89
|
700
|
50 days
|
Strontium-90
|
64
|
29 years
|
Zirconium-95
|
1,200
|
64 days
|
Ruthenium-103
|
1,200
|
39 days
|
Ruthenium-106
|
390
|
370 days
|
Iodine-129
|
46
|
16 million years
|
Tellurium-132
|
4,000
|
78 hours
|
Xenon-133
|
420,000
|
5 days
|
Cesium-137
|
42
|
30 years
|
Cerium-144
|
3,800
|
284 days
|
Plutonium-239
|
1.8
|
24,000 years
|
Estimates of Radiation Released into the Columbia River by Hanford, 1944-1971
Amount Released (curies)11
|
half-life
| |
Sodium-24
|
13,000,000
|
15 hours
|
Phosphorus-32
|
230,000
|
14 days
|
Scandium-46
|
120,000
|
84 days
|
Chromium-51
|
7,200,000
|
28 days
|
Manganese-56
|
80,000,000
| |
Zinc-65
|
490,000
|
245 days
|
Gallium-72
|
3,700,000
|
14 hours
|
Arsenic-76
|
2,500,00
|
26 hours
|
Yttrium-90
|
450,000
|
64 hours
|
Iodine-131
|
48,000
|
8 days
|
Neptunium-239
|
6,300,000
|
2.4 days
|
Soil and Groundwater Contamination12
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, about 60 million gallons of highly radioactive waste from the chemical separations plants are stored in 177 underground tanks at Hanford. The tanks contain about 200 million curies of radioactivity. Over the years, more than 1 million gallons, containing over 100,000 curies of radioactivity, have leaked into the soil. At present, it is uncertain whether any of this waste has reached the groundwater.
In contrast to the tank wastes, it is known that much of the groundwater underneath Hanford has been contaminated by radioactive process wastes. The separations plants required large amounts of water to process plutonium and this water became contaminated inside the plants. Hanford has estimated that over 440 billion gallons of these radioactive wastes were dumped into the ground. Some radioactive materials traveled through the soil and entered the groundwater. During Hanford's early years, other radioactive wastes penetrated the groundwater through "injection wells," or shafts drilled deep into the ground.
Tritium is the most commonly found radionuclide in the groundwater at Hanford. Ruthenium-106, technetium-99 and iodine-129 are three of the other radioactive materials commonly found in Hanford's groundwater. Some radioactive substances still remain in the soil and may enter the groundwater in the future.
HEDR concluded that there was little human contact with the contaminated groundwater in the past. In the future, Hanford's groundwater contamination could pose a danger to the public.
Hanford also buried solid wastes in the soil. This waste contains nearly 5 million curies of radioactivity.
TRITIUM POLLUTION INTO WATER AND AIR RESOURCES FROM REACTORS
Dose-to-third party
Doses
to the public can arise by two possible means. Firstly, controlled release of radioactive
substances to air and water within clearly regulated and safe limits is normal
during operation of facilities in the nuclear fuel cycle. If this activity were
to reach the food chain it could cause a dose to members of the public.
Discharges from Sizewell B are monitored and are subject to strict control by
the Environment Agency, which issues authorizations specifying the maximum
limits within which discharges should be kept. The annual discharge limits for
Sizewell B in 2002 are shown in Table 11 below, along with values expressed per
kWh. Note that act discharges are less than these values.
Table 11
Discharge Authorisation Limits
This table indicates that people living very near Candu reactors can
receive large amounts of tritium, with annual intakes of 1 million Bq per year
of HTO and a third of a million Bq per year of OBT. These values are 500 to
1,400 times greater than Canadian background levels. They indicate that people
living very near Candu reactor sites who eat produce from their gardens are
likely to be highly contaminated with tritium. In comparison, Osborne (2002)
estimated that the intakes of those living very close to Candu reactors were
two thirds of a million Bq per year of HTO and 42,000 Bq of OBT. These are not
too different from the above estimates. Notice that about 90% of their tritium
(water) intake is from food and if the OBT from food is added, it can be seen
that almost all their tritium intake is from food. These results are summarised
in tables 8.5 and 8.6. (Tritium in Gas form(HT), in water form (HTO), in organic form in foods (OBT)
A dose factor converts each Bq of a nuclide to a radiation “dose”
expressed in sieverts (Sv). One then compares this calculated dose to the present
Canadian public dose limit of 1,000 microsieverts (μSv) per year.
The problem, and here we get to the nub of the matter, is that the
official dose factors for HTO and OBT are the smallest (by considerable
margins) of all common radionuclides. For example, the ingestion dose
coefficient for tritiated water (1.8 x 10-11 Sv per Bq) is ~700 times lower than that for Cs-137, a common man-made
radionuclide. When tritium’s tiny dose factors are used to calculate doses, the
resulting doses are miniscule. For example, according to official dose factors,
the highest exposed persons in Table 8.4 above only receives about 20 μSv per
year from tritium (i.e., 50 times lower than the annual 1000 μSv safety limit).
Therefore Canadian health agencies and radiation regulators consider tritium discharges
not to be dangerous.
When there is no minium radiation dose to cause health effects how can we set a safety standard?
http://www.greenpeace.org/canada/Global/canada/report/2007/6/tritium-hazard-report-pollu.pdf
http://www.pnl.gov/main/publications/external/technical_reports/PNNL-15614.pdf
While Canada presents true facts on radioactive discharges into air and water Indian experts of NPCIL present highly underestimate radioactive emissions from the reactors to mislead people. See the following website to know how actual reactor emissions are lower than background ones
http://www.npcil.nic.in/pdf/news_28sep2011_02.pdf
RUSSIAN VERSION OF KUDANKULAM REACTORS
http://www.atomstroyexport.com/project/eng/23
In the south of India Atomstroyexport JSC successfully constructs Kudankulam NPP with two power units with reactor plants VVER-1000. The plant is constructed within the framework of implementation of the Intergovernmental Agreement and a Supplement to it dated 21.06.1998. The customer is Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL).
The first group of Russian
specialists commenced the work at the NPP construction site in October
2002. According to the contracts the scope of obligations of
Atomstroyexport JSC includes development of working, start-up and
adjustment and operational documentation, design supervision for NPP
buildings and structures construction; supply of equipment and materials
from Russia and third countries; technical support during the NPP
erection and commissioning; training of Indian operational and
maintenance personnel in Russia.
ABOUT THE DESIGN
NPP-92 design applicable at
Kudankulam NPP was developed by Atomenergoproject Institute (Moscow) on
the basis of serial power units, which have been operated in Russia and
the countries of Eastern Europe for a long time. The main distinctive
feature of the design is application of updated equipment and
introduction of additional passive safety systems in combination with
active traditional and new systems enhancing the plant’s safety.
The reactor plant is in double
containment which prevents radioactivity emission in the environment,
and protects the reactor plant from natural and man-made external
impacts such as an earthquake, tornado, hurricane, blast wave, airplane
crash, etc.
What about sabotage, bombing, terrorist attacks, suicidal squads etc.,?
http://www.aerb.gov.in/T/PUBLICATIONS/CODESGUIDES/sg-s-1.pdf
http://www-ns.iaea.org/downloads/rw/meetings/environ-consequences-report-wm-08.05.pdf
http://www.stanford.edu/group/efmh/jacobson/TenHoeveEES12.pdf
RECOMMENDED INTERVENTION LEVELS FOR URGENT
PROTECTIVE ACTIONS
Protective
action
|
Genenc
intervention level
(dose
avertable by the protective action)!Lb
|
Sheltenng
|
10mSv
|
Evacuation
|
50
mSv
|
Iodine
prophylaxis
|
100
mGy
|
Temporary
relocation
|
30 mSv in first 30 days
10
mSv in a subsequent 30 days
|
Permanent
resettlement
|
1
Sv in lifetime
|
SUGGESTED
URGENT AND LONGER TERM PROTECTIVE ACTION PLANNING ZONE SIZES
FACILITY
CATEGORY
|
PRECAUTIONARY
ACTION ZONE
SIZE
(PAZ)
|
URGENT
PROTECTIVE
ACTION
PLANNING ZONE
SIZE (UPZ)
|
LONGER TERM
PROTECTIVE
ACTION
PLANNING ZONE
SIZE (LPZ)
|
CATEGORY I
|
3-5 km
|
10-25 km
|
50- 100 km
|
CATEGORY II
Large
distances are for facilities in the
top half of the rang
|
On-site
|
0 5-1 km
|
5-10 km
|
On-site
|
1 5-2 km
|
15-20 km
|
|
CATEGORY IE
|
On-site
|
Not required
|
Not required
|
http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/article3808724.ec
http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/article3808724.ece
CAG Report condemns AERB on its malfunctioning in ensuring safety
http://blogs.reuters.com/india/2012/08/28/is-indias-nuclear-safety-worth-only-500-rupees/
ROUTINE RELEASES OF RADIOACTIVITY FROM NUCLEAR PLANTS INTO AIR AND WATER
http://books.google.co.in/books?id=QUmazo6y26sC&pg=PA46&lpg=PA46&dq=normalized+release+of+radionuclides+from+nuclear+power+stations&source=bl&ots=4loUS0CWfC&sig=NT7M0qBEd2xKZwZ-nQ5JAp2QEjc&hl=en&sa=X&ei=cjmJUM6iKYvorQfM34CQBg&ved=0CDsQ6AEwBQ#v=onepage&q=normalized%20release%20of%20radionuclides%20from%20nuclear%20power%20stations&f=true

PRIOR TO STARTING KUDANKULAM REACTORS EMERGENCY EXERCISES
MUST BE CONDUCTED ONCE
NRC NEWS
U.S.
NUCLEAR REGULATORY COMMISSION
Office of
Public Affairs Telephone: 301/415-8200
Washington,
D.C. 20555-0001
E-mail:
opa.resource@nrc.gov Site: www.nrc.gov
Blog:
http://public-blog.nrc-gateway.gov
|
|
No. 11-050
|
March 16,
2011
|
NRC PROVIDES PROTECTIVE ACTION
RECOMMENDATIONS BASED ON U.S. GUIDELINES
Under the
guidelines for public safety that would be used in the United States under
similar circumstances, the NRC believes it is appropriate for U.S. residents
within 50 miles of the Fukushima reactors to evacuate.
Among other
things, in the United States protective actions recommendations are implemented
when projected doses could exceed 1 rem to the body or 5 rem to the thyroid. A
rem is a measure of radiation dose. The average American is exposed to
approximately 620 millirems, or 0.62 rem, of radiation each year from natural
and manmade sources.
In making
protective action recommendations, the NRC takes into account a variety of
factors that include weather, wind direction and speed, and the status of the
problem at the reactors.
Attached are
the results of two sets of computer calculations used to support the NRC
recommendations.
In response to nuclear emergencies, the NRC works with other
U.S. agencies to monitor radioactive releases and predict their path. All the
available information continues to indicate Hawaii, Alaska, the U.S.
Territories and the U.S. West Coast are not expected to experience any harmful
levels of radioactivity.
Maximum
Dose Values (rem) - Close-In - To 50
miles(in numerical figures)
Distance from release
(miles/Km)
|
1.5 miles 2.4 Km
|
7miles 11km
|
10miles 16km
|
20miles 32km
|
30miles 48km
|
40miles 64km
|
50miles 80km
|
Total EDE
|
1200
|
160
|
95
|
63
|
37
|
18
|
8
|
Thyroid CDE
|
6200
|
840
|
510
|
270
|
130
|
59
|
23
|
Inhalation CEDE
|
800
|
110
|
67
|
31
|
13
|
4.4
|
1.3
|
Cloudshine
|
5.8
|
1
|
0.6
|
0.4
|
0.2
|
0.07
|
0.03
|
4-day Groundshine
|
380
|
46
|
38
|
32
|
24
|
13
|
7
|
Inter Phase 1st year
|
5400
|
660
|
590
|
480
|
380
|
220
|
130
|
Inter Phase 2nd year
|
2600
|
310
|
280
|
230
|
180
|
110
|
69
|
TEDE - Total Effective Dose
Equivalent CDE - Committed Dose Equivalent CEDE -
Committed Effective Dose Equivalent PAGs – Protective Action Guidelines EPA –
Environmental Protection Agency
• Doses exceeding PAGs are underlined.
• Early-Phase PAGs: TEDE - 1 rem, Thyroid (iodine) CDE - 5 rem
• Intermediate-Phase PAGs: 1st year - 2 rem, 2nd year - 0.5 rem
• *** indicates values less than 1 mrem
• To view all values - use Detailed Results | Numeric Table
• Total EDE = CEDE Inhalation + Cloudshine + 4-Day Groundshine
• Total Acute Bone = Bone Inhalation + Cloudshine + Period
Groundshine
MODEL
CALCULATION BY AERB FOR DISPERSAL OF STACK EMISSION OF RADIONUCLIDES UNDER
SPECIFIED CONDITIONS
Isotope I-131
Half life
Source
strength
Terrain
Stack height
Atmospheric
stability
Wind speed at
stack level
Wind direction
Deposition velocity
|
I-131
8.05
days
102
Bq/s (100 Bq/Sec)(continuous, release)
Flat
100
m
category
D
3
m/s
NW
2
x 10-3 m/s
|
|
Downwind
distance
from
stack (km)
|
Sector
averaged ground level air Concentration
(Bq/m3)
|
Ground
level
deposition
rate (Bq/m2s)
|
0.1
|
00.0E00
|
0.00(-00)
|
0.2
|
3.29E-31
|
6.58
(-34)
|
0.5
|
2.82E-09
|
5.64
(-12)
|
1.0
|
1.39E-05
|
2.78
(-08)
|
1.6
|
7.05E-05
|
1.41
(-07)
|
3.0
|
9.53E-05
|
1.91
(-07)
|
5.0
|
6.83E-05
|
1.37
(-07)
|
10.0
|
3.83E-05
|
7.66
(-08)
|
FUKUSHIMA STACK EMISSIONS (Bq) AND IMPACT DOSES IN mSv
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/te_1638_web.pdf
There are authorized discharge limits for a number of specific and groups of radionuclides. For nuclear power plants, the upper value for dose constraint received by the public is set to 0.25 mSv/a by the national standard Regulations for environmental radiation protection of nuclear power plants (GB 6249-86). Under this dose constraint, the discharge quantity limits are also set by GB 6249-86, shown in Table 7. In the review version of GB 6249-86 (GB 6249-200x), the derived discharge activity concentration limits are expected to set as 3700 Bq/L for NPP in shore, 370 Bq/L for NPP in inland.
CZECH LIMITS (SPECIAL)
The dose constraint for a total discharge of radioactive substances from a practice is an average effective dose of 250 μSv per year for a member of a critical group of public, for nuclear power plants (200 μSv for airborne discharges and to 50 μSv for watercourse discharges). Nuclear power plants are required to perform an optimization process and, on the basis of its results, the SUJB sets authorized discharge limits for the NPP. The authorized discharge limits are site specific. Current authorized limits for NPP Dukovany are 40 μSv for airborne discharges and 6 μSv for watercourse discharges; and for NPP Temelín 40 μSv for airborne discharges and 3 μSv for watercourse discharges.
GLC VARIES BASED ON VARIATIONS OF EXIT VELOCITIES AND EMISSION QUANTITIES:
Table 18 shows the results from CAP-88 calculations when the stack gas velocity is varied between 9 and
36 m3/s by varying the flow rate of stack gas without changing the radionuclide input rate. In this case,
two parameters change: the stack gas velocity and the radionuclide concentration in the stack gas. When
the nominal 18 m/s stack gas velocity is reduced to half its nominal value and the stack gas radionuclide
concentration is increased to twice its nominal concentration, then the total dose increases by 21%. When
the nominal 18 m/s stack gas velocity is doubled (and the stack gas radionuclide concentration is
decreased to half its nominal value), then the total dose decreases by 29%.
http://www.inl.gov/technicalpublications/Documents/5427530.pdf

http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/INES-2009_web.pdf
Table 2gives conversion factors for radiological equivalence to 131I that should be used. The actual activity of the isotope released should be multiplied by the factor given in Table 2 and then compared with the values given in the definition of each level. If several isotopes are released, the equivalent value for each should be calculated and then summed (see examples 5–7). The derivation of these factors is explained in Appendix I.
CONVERSION UNITS BECQUEREL TOSIEVERTS
Conversion of
Becquerel to millisievert
The
contamination of soil, food and water is given in Becquerel/sq.metre or
Becquerel/Kg or litre. [58]
Becquerel (Bq)
means one disintegration per second.
The Becquerel (Bq) measures the activity of radioactive substances, whereas the Sievert (Sv) evaluates the effects of radiation on the body.
A measure of
the biological damage to living tissue as a result of radiation exposure.
Also known as the " biological dose," the dose equivalent is
calculated as the product of absorbed dose in tissue multiplied by a quality
factor and then sometimes multiplied by other necessary modifying factors at
the location of interest.
The dose
equivalent, measured in sievert, defined as the dose of absorbed radiation
that has the same biological effect as a dose of one joule of gamma rays
absorbed in one kilogram of tissue. In the United States the roentgen
equivalent man (rem), equal to 0.01 sievert, is still in common use, although
regulatory and advisory bodies are encouraging transition to sieverts
1 Bq
= 0,0125 microsievert
1 microsievert = 80 Becquerel = 1mSv = 80,000 to 1,00,000Bq/sq.m
Eating an
amount of food with 80.000 Becquerel Caesium 137 is equivalent to
approximately one millisievert.
Eating 200 g mushrooms contaminated with 4.000 Becquerel Caesium 137/Kg s equivalent to 0,01 Millisievert.
The radiation
exposure considers how long the exposure took place. It is given in
Millisievert/year. Example; The natural radiation exposure in Germany is 2,1
Millisievert/year (0,24 Microsievert/hour) another 2Millisievert are added as
artificial radiation (mainly medical devices)
Food radiation
should not exceed 500 Becquerel/Kg
Baby food radiation should not exceed 400 Becquerel/Kg for Caesium and 100 Becquerel for iodine |
Sample calculation:
Dose rate at 1foot = 10
millirem / hour
Dose rate at 3 feet = 10 x
(1/3) 2 or 1.1 millirem / hour
A person standing 3 feet
from the decedent for ½ hour would receive 0.5 millirem.
Avoid the use of
adjectives like “safe” or “dangerous.” Compare the estimated dose to a familiar
source like chest radiographs, airline flights, or dental radiographs
Examples of Radiation
Doses
|
Doses in millirad
|
1 year of gas range use
|
4
|
1 hour of airline flight
above 30,000
|
0.3
|
1 year of living in Maryland
|
15
|
1 year living in Colorado
|
65
|
1 chest x-ray
|
20
|
1 year exposure to naturally
occurring radioactive material in the human body
|
40
|
1 year exposure to background
radiation (all sources)
|
300
|
1 year regulated limit to a
member of the public
|
500
|
1 year regulated occupational
limit
|
5,000
|
Threshold for acute radiation
syndrome
|
50,000
|
50% Fatality dose
|
500,000
|

















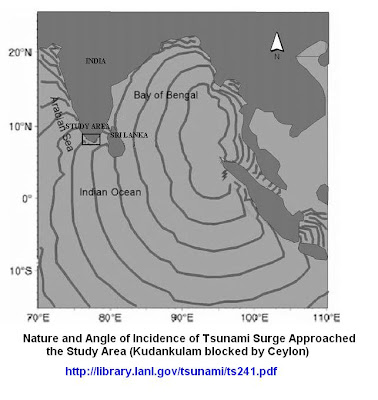
































5 comments:
sir it is very informative reading ur blog i am a architecture student doing my thesis on this kudankulam nuclear power plant would like to contact u regarding my thesis research,i request you to forward your e.mail id for me to contact you regarding my research.
thanking u
jaseer ali
jaseer_84@yahoo.co.in
mob:09765995001
Wonderful blog & good post.Its really helpful for me, awaiting for more new post. Keep Blogging!
Top Colleges in Tamilnadu
It is very informative reading your blog. It’s really helpful for me.
ACP sheet printing machine
This blog such a very good explanation.I can clearly understand the authors explains,thanks for sharing #ISO CERTIFICATION
#ISO 45001
#45001 LEAD AUDITOR COURSEIN CHENNAI
Nice blog
Swasti Enviro - Environmental Testing, Air Monitoring, Water Testing, Services, Chennai, Tamilnadu
Post a Comment